涤盖棉织物的短流程加工方法主要有3种,即精练与分散染料染涤一浴法、活性染料染棉与分散染料染涤一浴法、双氧水漂白棉与分散染料染涤一浴法[10-11]。其中,双氧水漂白棉与分散染料染涤工艺简称为漂染一浴法,是将涤盖棉织物的棉组分双氧水漂白和涤组分分散染料染色在一浴中进行,具有效率高、水耗,能耗低、绿色环保等特点[12-13],且染色织物手感更佳,是涤盖棉织物短流程加工的重点研究方向[14]。涤盖棉织物漂染一浴工艺的关键在于分散染料的选择,由于棉组分氧漂使用双氧水在碱性条件下进行,双氧水分解出的过氧氢根离子具有比氢氧根离子更强的亲核攻击能力,因此要求分散染料既要具有耐碱性也要具有良好的耐氧漂性[15]。在常规分散染料中筛选具有耐碱、耐氧漂性能的分散染料,用于涤盖棉织物的漂染一浴加工具有可行性[16-17],但目前筛选出的耐碱耐氧漂分散染料品种较少、色谱不全。
本文使用实验室合成的高耐碱高耐氧漂分散蓝、红、黄3只染料,简称为HAO分散蓝、HAO分散红和HAO分散黄,对涤盖棉织物进行漂染一浴加工,分析关键工艺对涤盖棉织物中棉组分白度及涤组分颜色深度的影响,确定漂染一浴最佳工艺,并对涤盖棉织物吸湿性、顶破强力、颜色性能和色牢度进行测试。
1 实验部分
1.1 实验材料和仪器
织物:涤盖棉针织坯布,正面为涤纶组分,反面为棉组分,涤纶与棉比例为55:45,涤纶纱线线密度为109 dtex(48 f),棉纱线线密度为35.6 tex,面密度为260 g/m2,由莱美科技股份有限公司提供。
材料:HAO分散蓝、HAO分散红、HAO分散黄(纯度分别为98%、98%、97%),实验室合成,结构式如图1所示;使用时,将染料进行商品化加工成为商品染料。保险粉、氢氧化钠、碳酸钠、醋酸钠、醋酸,双氧水(质量分数为30%),碳酸氢钠,均为分析纯,由国药集团化学试剂有限公司提供;高温高压染色用分散匀染剂,工业纯,由日华化学有限公司提供;渗透剂JFC,双氧水稳定剂DM-1403,精练剂DM-1346,均为工业纯,由广东德美精细化工有限公司提供;皂片,工业纯,由上海制皂厂提供。
图1
图1
HAO分散蓝、红、黄染料化学结构式
Fig.1
Chemical structures of HAO Disperse Blue (a), HAO Disperse Red (b) and HAO Disperse Yellow (c)
仪器:Ahiba IR红外小样染色机、Datacolor 800分光光度仪、Datacolor 800测色配色仪(美国Datacolor公司),HD026N电子织物强力机(常州市天祥纺织仪器有限公司),SW-24E耐洗色牢度试验机(无锡纺织仪器厂),Y(B) 571-II耐摩擦色牢度试验机(温州市大荣纺织标准仪器厂),Gellowen G247升华色牢度实验仪(无锡纺织机械公司)。
1.2 染色处方与工艺流程
1.2.1 涤盖棉织物传统两浴两步法工艺
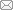
练漂棉处方为:精练剂1 g/L;双氧水稳定剂2 g/L;双氧水4 g/L;氢氧化钠1.6 g/L;渗透剂JFC 3 g/L;浴比1:30。
染色处方为:分散染料2%(o.w.f);匀染剂1 g/L;调节染浴pH值4.8;浴比1:30。
还原清洗及皂洗工艺处方为:烧碱2 g/L,保险粉2 g/L,浴比1:30,温度85 ℃,时间10 min;皂片3 g/L,温度90 ℃,时间10 min,浴比1:30。
涤盖棉织物漂棉染涤两浴两步法工艺曲线如图2所示。
图2
图2
涤盖棉织物漂棉染涤常规工艺流程
Fig.2
Conventional process of polyester-covered cotton fabric for cotton bleaching and polyester dyeing
1.2.2 涤盖棉织物漂染一浴一步法工艺
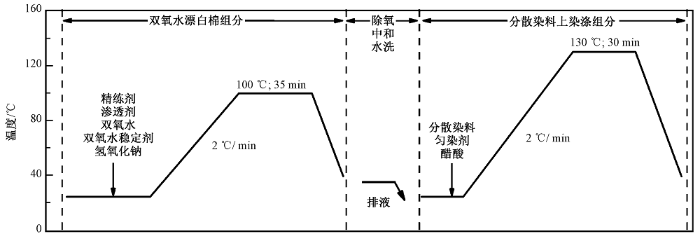
工艺处方为:分散染料2%(o.w.f);匀染剂1 g/L;精练剂1 g/L;双氧水稳定剂2 g/L;双氧水0、1、2、4、6、8 g/L;氢氧化钠0、0.4、0.8、1.6、2.4、3.2 g/L;渗透剂JFC 3 g/L;浴比1∶30。
图3
图3
涤盖棉织物漂染一浴工艺流程
Fig.3
One-bath process for cotton bleaching and polyester dyeing of polyester-covered cotton fabric
图4
图4
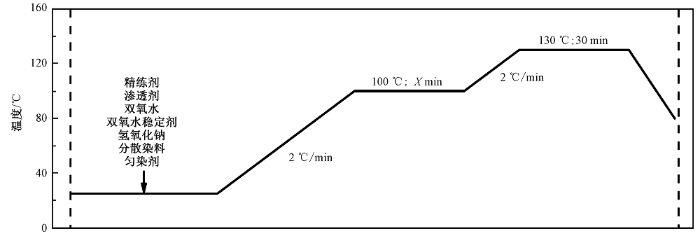
涤盖棉织物漂染一浴工艺加工步骤
Fig.4
One-bath process of polyester-covered cotton fabric for cotton bleaching and polyester dyeing
1.3 测试方法
1.3.1 分散染料的耐碱性及耐氧漂性测试
1.3.2 表观色深及色差测试
使用分光光度仪测定试样表观色深(K/S)值。选用D65为标准光源,在10°视场下观察,在折叠成4层的织物上测量4次取平均值获得涤盖棉织物正面涤纶组分在最大吸收波长处的K/S值和色差值ΔECMC。
1.3.3 白度值测试
涤盖棉织物内层棉组分的白度使用测色配色仪参照AATCC 110—2015《纺织品的白度》进行测量,并计算CIE白度指数。
1.3.4 吸湿性测试
涤盖棉织物的棉组分吸水性参照AATCC 79—2018《纺织品的吸湿性》,使用水滴法进行测量,并记录水滴在织物表面消失所需时间,检测处理后布样的精练程度,水滴润湿时间≤1 s时为合格,润湿时间>60 s时视为不易润湿。
1.3.5 染色织物相关性能测试
参照GB/T 19976—2005《纺织品 顶破强力的测定 钢球法》测定织物的顶破强力。参照GB/T 3921—2008《纺织品 色牢度试验 耐皂洗色牢度》测定织物的耐水洗色牢度。参照GB/T 3920—2008《纺织品 色牢度试验 耐摩擦色牢度》测定织物的耐摩擦色牢度。参照GB/T 5718—1997《纺织品 色牢度试验 耐干热(热压除外)色牢度》测定织物的升华色牢度。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 分散染料的耐碱性和耐氧漂性评估
2.1.1 分散染料的耐碱性
表1 分散染料耐碱性的评价标准
Tab.1
| 不同碱调节剂下的ΔECMC | 耐碱类型 | 等级 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH3COONa | Na2CO3 | NaOH | |||
| ΔECMC>1.0 | - | - | 不耐碱 | 差 | |
| ΔECMC≤1.0 | ΔECMC>1.0 | - | 耐弱碱 | 中 | |
| ΔECMC≤1.0 | ΔECMC≤1.0 | ΔECMC>1.0 | 一般耐碱 | 良 | |
| ΔECMC≤1.0 | ΔECMC≤1.0 | ΔECMC≤1.0 | 高耐碱 | 优 | |
表2 HAO分散染料的耐碱性评价
Tab.2
| 染料名称 | 不同碱调节剂下的ΔECMC | 耐碱 类型 | 等级 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH3COONa | Na2CO3 | NaOH | |||
| HAO分散蓝 | 0.19 | 0.49 | 0.55 | 高耐碱 | 优 |
| HAO分散红 | 0.29 | 0.32 | 0.34 | 高耐碱 | 优 |
| HAO分散黄 | 0.34 | 0.52 | 0.56 | 高耐碱 | 优 |
从表2可看出,与pH值为4.8的酸性浴染色对比,HAO分散蓝、红、黄3只染料在2 g/L NaOH碱调节剂染色浴中,染料染色涤盖棉织物涤组分的ΔECMC均小于1.0,为高耐碱型,耐碱性能均评为优。
2.1.2 分散染料的耐氧漂性
表3 分散染料的耐氧漂性评价标准
Tab.3
| H2O2和NaOH 溶液下的ΔECMC | 灰卡 级别 | 耐氧 漂性 | 是否可用于漂染 一浴工艺 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ΔECMC>1.0 | 低于4~5级 | 差 | 否 |
| ΔECMC≤1.0 | 不低于4~5级 | 优 | 是 |
表4 HAO分散染料的耐氧漂性评价
Tab.4
| 染料名称 | H2O2和NaOH 溶液下的ΔECMC | 灰卡 级别 | 耐氧 漂性 | 是否可用于漂染 一浴工艺 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HAO分散蓝 | 0.88 | 4~5级 | 优 | 是 |
| HAO分散红 | 0.62 | 5级 | 优 | 是 |
| HAO分散黄 | 0.82 | 4~5级 | 优 | 是 |
从表4可看出,与不含双氧水的染色浴对比,HAO分散蓝、红、黄3只染料在5 g/L的双氧水和2 g/L烧碱染色浴中,染色织物的ΔECMC均小于1.0,灰卡级别为4~5级,评估为耐氧漂性优异,均可用于涤棉织物漂染一浴工艺。
2.2 涤盖棉漂染一浴工艺影响因素分析
2.2.1 双氧水浓度和保温时间对K/S值与白度影响
图5
图5
双氧水质量浓度和保温时间对涤盖棉织物K/S值的影响
Fig.5
Influence of H2O2 concentrations and temperature maintaining time on K/S value of polyester-covered cotton fabric.
(a)HAO Disperse Blue; (b) HAO Disperse Red; (c) HAO Disperse Yellow
图6
图6
双氧水质量浓度和保温时间对涤盖棉织物白度的影响
Fig.6
Influence of H2O2 concentrations and temperature maintaining time on whiteness of polyester-covered cotton fabric.
(a)HAO Disperse Blue; (b) HAO Disperse Red; (c) HAO Disperse Yellow
2.2.2 双氧水浓度和保温时间对颜色深度的影响
由图5可以看出,HAO分散蓝、红和黄3只染料上染的涤盖棉织物涤组分的K/S值仅在某个值附近波动,可认为涤组分的色光几乎保持稳定。此外,分别使用HAO分散蓝、红和黄3只染料对涤盖棉织物进行常规工艺处理,得到涤组分的K/S值分别为25.36、23.65和13.41,与漂染一浴工艺处理后的涤组分K/S值几乎一致,ΔECMC均在1.0以下,因此可认为,在漂染一浴加工体系中,双氧水和其他漂白助剂的存在并未影响HAO分散蓝、红、黄3只染料的染色效果,且双氧水质量浓度及在100 ℃下的保温时间对这3只染料上染涤纶的K/S值没有影响。
由图6可以看出,在漂染一浴加工体系中,HAO分散染料及其它染色助剂的存在并未影响双氧水的漂白作用。双氧水质量浓度为2 g/L,保温时间为0 min时,涤盖棉织物棉组分的白度值就可达到工业及生活用品的加工要求,与传统工艺所得白度几乎无差别。再增加双氧水的用量,棉组分的白度值也几乎没有增加,因此最优的双氧水质量浓度是2 g/L,在100 ℃下的最佳保温时间是0 min。传统工艺常用质量浓度为4 g/L的双氧水对棉织物进行漂白,从室温升温至100 ℃后保温35 min,一般能使棉织物的白度值达到80左右[20]。漂染一浴工艺与传统漂白工艺处方存在差别的主要原因是,漂染一浴工艺会将温度逐步升至130 ℃,延长了双氧水的作用温度和时间,从而可减少双氧水的用量,漂白工艺中双氧水用量的降低可使后续除氧的难度大大降低。
2.2.3 加工时间和温度对白度和K/S值的影响
图7
图7
漂染一浴工艺加工时间对涤盖棉织物白度和K/S值的影响
Fig.7
Influence of processing time on whiteness and K/S value of polyester-covered cotton fabric.
(a)HAO Disperse Blue; (b) HAO Disperse Red; (c) HAO Disperse Yellow
从图7可以看出,在漂染一浴加工体系中,双氧水及漂白助剂、HAO分散染料及染色助剂同时存在的情况下,涤盖棉织物棉组分的漂白和涤组分的染色同时发生,棉组分的白度值和涤组分的K/S值均在130 ℃时达到最高值且之后趋于稳定。涤盖棉织物棉组分白度值在100~110 ℃时显著增大,到110 ℃时棉组分白度值已达到70左右,说明棉组分的漂白主要发生在这个阶段。而持续升温后,棉组分的白度值仍然不断增大,双氧水仍存在漂白作用,直至升温130 ℃,白度值达到稳定,主要原因是温度升高会加速双氧水的有效分解,从而提高了对色素的氧化反应速度,体现在白度值的快速增大[21]。而涤盖棉织物涤组分的K/S值在110~130 ℃时显著增大,130 ℃之后涤组分的K/S值几乎不发生变化,这与涤纶常规高温高压染色过程规律一致[22]。为提高织物的匀染性和透染性,将在130 ℃下保温时间确定为30 min。因而确定涤盖棉织物漂染一浴最佳工艺,即涤盖棉织物在含有质量浓度为2 g/L的双氧水和质量浓度为0.8 g/L氢氧化钠染浴中,升温至130 ℃后保温30 min。
2.3 涤盖棉织物各项性能分析
为探究涤盖棉织物经传统工艺和漂染一浴工艺处理后的各项性能是否存在差异,采用1.2.1节的工艺处方和步骤对涤盖棉织物进行处理,并与漂染一浴工艺作对比。分别测试经传统工艺和漂染一浴工艺处理的涤盖棉织物的各项性能,结果如表5所示。
表5 传统工艺和一浴工艺处理后涤盖棉织物的各项性能
Tab.5
| 染料 名称 | 工艺 | 顶破强 力/N | 棉组分 润湿时 间/s | 棉组分 白度值 | 涤组分 K/S值 | ΔECMC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 涤盖棉坯布 | 1 201 | >60 | 20.30 | 1.52 | — | |
| HAO 分散蓝 | 传统工艺 | 1 009 | ≤1 | 79.82 | 25.36 | 0.65 |
| 漂染一 浴工艺 | 1 106 | ≤1 | 78.20 | 26.15 | ||
| HAO 分散红 | 传统工艺 | 1 016 | ≤1 | 80.35 | 23.65 | 0.73 |
| 漂染一 浴工艺 | 1 098 | ≤ 1 | 79.68 | 24.02 | ||
| HAO 分散黄 | 传统工艺 | 1 064 | ≤ 1 | 78.34 | 13.41 | 0.47 |
| 漂染一 浴工艺 | 1 115 | ≤ 1 | 77.92 | 13.96 |
由表5可以看出,传统工艺处理的涤盖棉织物强力损失比漂染一浴工艺大,主要原因是传统工艺染涤组分的条件是高温高压弱酸条件,而棉组分不耐酸,在高温酸性及长时间加工条件下,棉组分被损伤,进而引起涤盖棉织物强力下降。漂染一浴工艺中,始终在碱性条件下处理,且加工时间明显缩短,涤盖棉织物的强力下降不超过8%。2种工艺处理后的涤盖棉织物中的棉组分吸湿性好,白度值均接近80,满足后续活性染料套染棉的要求;2种工艺处理后的涤盖棉织物中涤纶组分K/S值相差无几,ΔECMC均小于1.0,说明漂染一浴工艺能获得与传统工艺相同的颜色。因此,当从传统工艺转换为漂染一浴工艺时,无需过多打样实验就可以获得相同色光。
表6列出传统工艺和漂染一浴工艺处理后涤盖棉织物的色牢度。可以看出,漂染一浴工艺处理后的涤盖棉织物耐摩擦、耐水洗及耐升华色牢度与传统工艺相差不大,且除耐升华色牢度中沾色有4级外,其他的各项色牢度均达到4~5级到5级,完全满足生产需要。
表6 传统工艺和一浴工艺处理后涤盖棉织物的色牢度
Tab.6
| 染料 | 工艺 | 耐摩擦色牢度 | 耐水洗色牢度 | 耐升华色牢度 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干摩擦 | 湿摩擦 | 沾色 | 褪色 | 沾色 | 褪色 | ||
| HAO 分散蓝 | 传统工艺 | 5 | 4~5 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 4~5 |
| 漂染一 浴工艺 | 5 | 4~5 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 4~5 | |
| HAO 分散红 | 传统工艺 | 5 | 4~5 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 4~5 |
| 漂染一 浴工艺 | 4~5 | 4~5 | 5 | 4~5 | 4 | 4~5 | |
| HAO 分散黄 | 传统工艺 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 4~5 | 4~5 | 4~5 |
| 漂染一 浴工艺 | 4~5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 4~5 | 4~5 | |
3 结论
1)本文合成的HAO分散蓝、红、黄3只染料经评估具有优异的耐碱性和耐氧漂性,属高耐碱高耐氧漂分散染料,使用这3只染料可将涤盖棉织物的棉组分练漂与涤组分染色合并在一浴实施。
2)采用HAO分散蓝、红、黄3只染料对涤盖棉织物进行漂染一浴加工,得到优化后的工艺:双氧水质量浓度为2 g/L,处理温度为130 ℃,保温时间为30 min;
3)漂染一浴工艺处理的涤盖棉织物,强力下降不超过8%,棉组分吸湿性好,白度值接近80,能够满足后续活性染料套染棉的要求;涤组分颜色与传统工艺一致,耐摩擦、耐水洗色牢度均不低于4~5级,耐升华色牢度不低于4级。
参考文献
涤盖棉单向导湿织物的加工
[J].
Manufacture of one way moisture conducted PTE/cotton knitted fabric
[J].
涤盖棉单向导湿校服面料的开发
[J].
Development of one way moisture conducted PTE/cotton knitted fabric on school uniform fabric
[J].
Smart color-changing textile with high contrast based on a single-sided conductive fabric
[J].DOI:10.1039/C5TC02983J URL [本文引用: 1]
One-bath one-step dyeing of a polyester/cotton blend using the pad-dry-fixation process
[J].
Dyeing properties of polyester/cotton blended fabric in the silicone non-aqueous dyeing system
[J].
DOI:10.14504/ajr.8.S2.2
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Polyester/cotton blended fabrics have been extensively used in the textile industry. However, the dyeing process of polyester/ cotton blended fabrics is complex, and a large amount of water is consumed. To increase the dye uptake and dye fixation ratio, and reduce wastewater effluents, the dyeing performance of polyester/cotton blended fabric was studied in one bath and two steps using the silicone non-aqueous dyeing system. When dyeing 1 kg of polyester/cotton blended fabric, only 1.17 kg of water was consumed, and no wastewater was discharged after dyeing. The washing fastness, staining fastness, and dry and wet rubbing fastness of dyed fabric can reach high levels. The dyeing performance of two disperse dyes on the cotton and polyester components in the blended fabric was also studied.
涤棉工装面料的节约型染整加工
[J].
Economical dyeing process of T/C blended working-wear fabric
[J].
针织物节能减排漂染工艺探讨
[J].
Practical technology of energy saving and emission reduction bleaching and dyeing of knitted fabrics
[J].
Benzyl-containing azobenzene-based disperse dyes: relationship between molecular packing and alkali-resistant stability
[J].
Dyeing properties of the disperse dyes containing cyano group based on benzisothiazole for polyester fabrics under alkali condition
[J].
涤棉针织物一浴一步法染色工艺研究
[J].
One-bath and one-step dyeing process of polyester-cotton knitted fabric
[J].
涤/棉织物分散/活性染料一浴法染色技术
[J].
One-bath dyeing technology of polyester/cotton fabric with disperse/reactive dyes
[J].
涤纶织物的练漂染一浴短流程技术
[J].
Scouring-bleaching and dyeing of polyester fabric in one bath
[J].
Development and application of polyester/cotton blended fabric dyes
[J].DOI:10.2115/fiberst.2016-0025 URL [本文引用: 1]
Synthesis of benzothiazole-azo disperse dyes for high resistance to alkaline treatments and peroxide bleaching
[J].
涤棉针织物炼漂染一浴工艺
[J].
One bath process of bleaching and dyeing for polyester/cotton knitted fabrics
[J].
涤棉氧漂染色一浴剂RY-236的应用与实践
[J].
Application and practice of oen bath reagent RY-236 for terylene/cotton oxygen bleaching dyeing
[J].
分散染料耐碱性能评定方法的研究
[J].
Research on alkaline resistance performance evaluation method of disperse dyes
[J].
分散染料耐氧漂性能的评定
[J].
Evaluation of disperse dyes for resistance to peroxide bleaching
[J].
Establishing a rapid pad-steam process for bleaching of cotton fabric with an activated peroxide system
[J].






 京公网安备11010502044800号
京公网安备11010502044800号