相较传统水基染色工艺,超临界CO2流体染色技术以临界点以上的CO2为介质,实现了水资源零消耗[3];染色无需添加各类助剂,CO2与剩余染料可回收循环利用[4];在实现染色过程中零用水、零污染[5]的同时,进一步减少了温室气体排放,符合当前绿色发展理念。目前,聚酯纤维[6]、筒纱[7]的超临界CO2无水染色技术日趋成熟,已处于产业化前期研究阶段,显示了较为明显的节水节能优势,但对于针织鞋材超临界CO2无水染色性能目前鲜见报道。特别是针织鞋面材料在穿着过程中,易受到复杂的挤压、摩擦等外力作用,相比服用织物,具有更高的物理性能要求。前期研究发现,在不同温度与压力下,超临界CO2对聚酯纤维具有各异的增塑、溶胀作用[8],易引起纤维物化性能的改变。
本文以超临界CO2为介质,利用分散黄54对涤纶针织鞋材进行染色,系统研究了不同温度、压力、时间、CO2流量对针织鞋材染色性能的影响。同时,重点探究了染色前后涤纶针织鞋材弯曲、收缩、摩擦、拉伸、耐用性能,以期为针织鞋材超临界CO2无水染色生产提供数据参考。
1 实验部分
1.1 实验材料与仪器
织物:涤纶针织鞋材,纱线线密度为12 tex,面密度为302 g/m2,信泰(福建)科技有限公司。
染料:分散黄54滤饼,相对分子质量为289.28,浙江龙盛集团股份有限公司;CO2气体(纯度为99%),中昊光明化工研究设计院有限公司。
仪器:超临界CO2流体染色设备,自制;Color-Eye7000A计算机测色仪,美国爱色丽公司;YG821L织物风格仪器,大原电子仪器公司;YG026B电子织物强力机,宁波纺织仪器厂;SW8A耐洗色牢度试验机,无锡纺织实验厂;YG571B耐摩擦色牢度试验机,温州际高检测仪器有限公司。
1.2 染色工艺
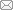
超临界CO2流体染色工艺流程如图1所示。将针织鞋材缠绕于染色经轴上,装于染色釜内,将染料放入染料釜内。利用加压泵将CO2注入系统内,开启换热器。当达到实验所需温度、压力后,关闭加压泵,打开循环泵。超临界CO2携带染料经染料釜、染色釜、循环泵、换热器,实现循环染色。染色结束后泄压回收CO2,从而实现CO2循环利用。
图1
染色处方:染料用量为1%(o.w.f);染色工艺曲线见图2。
图2
1.3 测试方法
1.3.1 表观色深值与匀染性测试
将染色后的针织鞋材对折2次,采用计算机测色仪进行K/S值测试,根据Kubelka-Munk公式计算染料在最大吸收波长处的K/S值[9],每个试样测试3次,结果取平均值。
式中:K为针织鞋材的吸收系数,L/(g·cm-1);S为针织鞋材的散射系数,L/(g·cm-1);R为最大吸收波长处针织鞋材的反射率,%;k为常数;q为染料与织物质量的比值,%。
按照下式计算染色鞋材的色深偏差值
式中:λ为染料的最大吸收波长,nm;i为染色织物编号;n为织物测色点个数。
1.3.2 染色色牢度测试
根据GB/T 3920—2008《纺织品 色牢度试验耐摩擦色牢度》,取50 mm×140 mm样品,采用耐摩擦色牢度试验机进行干摩擦和湿摩擦实验,测试染色针织鞋材耐摩擦色牢度。
根据GB/T 3921—2008《纺织品 色牢度试验耐皂洗色牢度》,取100 mm×40 mm样品,采用耐洗色牢度试验机,测试染色针织鞋材耐皂洗色牢度。
1.3.3 织物弯曲性能测试
参考GB/T 18318—2009《纺织品 弯曲性能的测定》,取50 mm×55 mm样品5份,采用织物风格仪,测试染色针织鞋材弯曲性能。
1.3.4 织物收缩率测试
参考FZ/T 50050—2020《合成纤维工业长丝热收缩率试验方法》,织物横纵向各取5处比较长度变化,测试染色针织鞋材收缩率。
1.3.5 织物摩擦性能测试
参考FZ/T 01054—2012《织物表面摩擦性能的实验方法》,取210 mm×70 mm样品5份,采用织物风格仪,测试染色针织鞋材的摩擦性能,结果取平均值。
1.3.6 织物拉伸性能测试
根据GB/T 3923—2013《纺织品 织物拉伸性能 第1部分:断裂强力和断裂伸长率的测定(条样法)》,取200 mm×50 mm样品5份,采用电子织物强力机,拉伸速率为100 mm/min,测试染色针织鞋材拉伸性能,结果取平均值。
1.3.7 织物耐用性能测试
根据GB/T 19976—2005《纺织品 顶破强力的测定 钢球法》,取45 mm×45 mm样品5份,采用电子织物强力机,拉伸速率为300 mm/min,测试染色针织鞋材顶破强力,结果取平均值。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 染色性能分析
2.1.1 染色压力对针织鞋材K/S值的影响
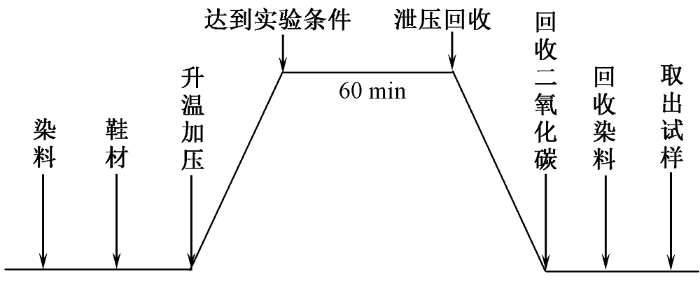
在染色温度为120 ℃,染色时间为60 min,CO2流量为400 kg/h的条件下,改变系统压力(18~26 MPa),进行鞋材超临界CO2无水染色,测定染色后针织鞋材的K/S值,结果如图3所示。
图3
图3
压力对针织鞋材K/S值的影响
Fig.3
Influence of pressure on K/S values of knitted shoe material
压力为18~24 MPa时,随着压力的逐渐升高,针织鞋材的K/S值明显增大。这是因为染料溶解度会随着温度、压力变化而变化[11-12],压力升高使得超临界CO2流体密度随之增大,提升了分散染料在超临界CO2流体中的溶解度[13],鞋材可吸附染料量增加。同时,CO2蒸汽压增大使其传质推动力上升,扩散效率增加,涤纶溶胀程度增大[14],染料更易进入纤维内部,上染量得到提升。但染料的上染是一个吸附与解吸动态平衡过程[15],随着压力升高,染料解吸作用也随之增强。当压力高于24 MPa时,染料吸附速率与解吸速率基本达到平衡,涤纶鞋材的K/S值趋于稳定;且色深偏差值Sλ波动皆稳定在0.1±0.05以内,可认为具有良好的匀染性。
2.1.2 染色温度对针织鞋材K/S值的影响
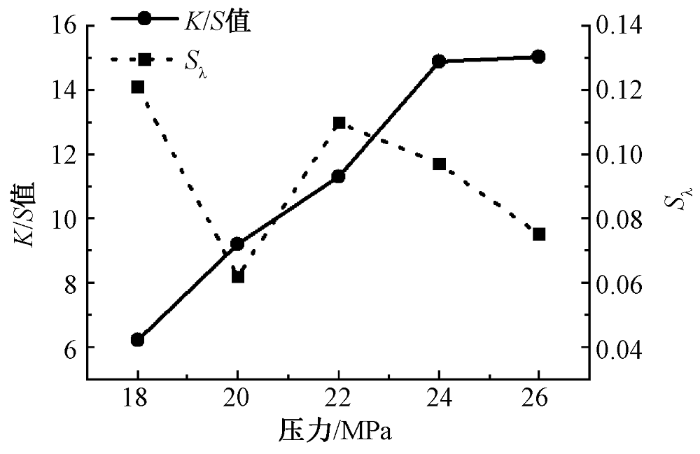
在染色压力为24 MPa,染色时间为60 min,CO2流量为400 kg/h的条件下,改变系统温度(105~125 ℃),进行鞋材超临界CO2无水染色,测定染色后针织鞋材的K/S值,结果如图4所示。
图4
图4
温度对针织鞋材K/S值的影响
Fig.4
Influence of dyeing temperature on K/S values of knitted shoe material
温度在105~120 ℃之间时,随着温度的上升,染色后针织鞋材的K/S值明显增大。依据超临界CO2无水染色理论可知,分散染料上染涤纶符合自由体积扩散模型[16]。针对染料分子而言,温度影响染料分子在超临界CO2中的聚集状态,若聚集体尺寸大于纤维微孔尺寸,则会导致染料分子难以扩散入纤维内部,温度上升致使染料单分子动能增加,聚集体解聚分散,从而提升染料的溶解扩散能力[17]。针对涤纶鞋材而言,温度升高加剧了涤纶大分子链的振荡,无定形区的空隙增大,染料分子更易于向纤维内部扩散[18]。但等压条件下继续升高温度,则会降低混合体系密度,进而导致流体溶解与扩散能力下降[8]。当温度达到120 ℃时,涤纶鞋材的K/S值趋于稳定;且Sλ幅度稳定在0.1上下,具有良好的匀染性。
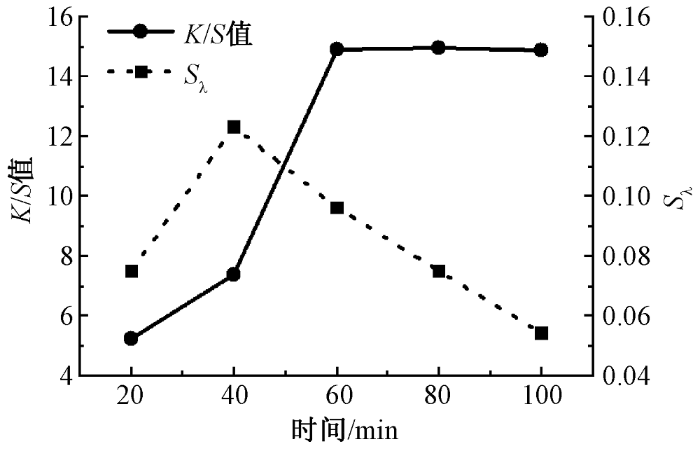
2.1.3 染色时间对针织鞋材K/S值的影响
在染色压力为24 MPa,染色温度为120 ℃,CO2流量为400 kg/h的条件下,改变染色时间(20~100 min),进行鞋材超临界CO2无水染色,测定染色后针织鞋材的K/S值,结果如图5所示。
图5
图5
染色时间对针织鞋材K/S值的影响
Fig.5
Influence of dyeing time on K/S values of knitted shoe material
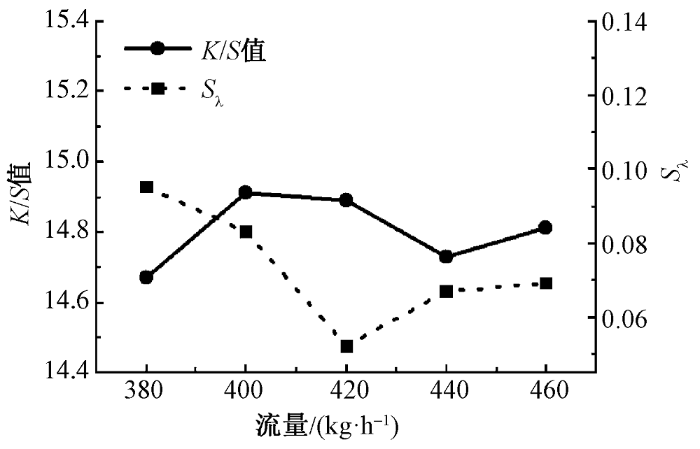
2.1.4 CO2流量对针织鞋材K/S值的影响
在染色压力为24 MPa,染色时间为60 min,染色温度为120 ℃条件下,改变CO2流量(380~460 kg/h),进行鞋材超临界CO2无水染色,测定染色后针织鞋材的K/S值,结果如图6所示。
图6
图6
CO2流量对针织鞋材K/S值的影响
Fig.6
Influence of CO2 flow on K/S values of knitted shoe material
由图6可知,CO2流量对涤纶针织鞋材的K/S值影响不大,随着CO2流量的逐渐增加,染色针织鞋材的K/S值基本不变。一方面,超临界CO2的增塑作用使涤纶鞋材的玻璃化温度降低[19],无定形区比例增加,提升了染料在超临界CO2中的上染量。另一方面,在一定的温度和压力下,染料在超临界CO2中的溶解度是有限的,继续增加CO2流量并不会增大染料的溶解度;同时,CO2流量提高也会缩短染料与织物的接触时间[18],在一定程度上阻碍了染料分子向纤维无定形区扩散渗透,从而影响织物在超临界CO2中的染色效果。因此,在双重作用下,降低了CO2流量对涤纶鞋材K/S值的影响;且Sλ波动幅度依旧稳定在0.1上下,具有良好的匀染性。
2.1.5 色牢度分析
表1示出不同温度下染色涤纶针织鞋材的色牢度指标。可知,染色后针织鞋材的耐皂洗色牢度达到4级以上,耐摩擦色牢度达到4~5级,满足国家标准要求。
表1 不同温度下针织鞋材的色牢度
Tab.1
| 温度/℃ | 耐摩擦色牢度/级 | 耐皂洗色牢度/级 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干 | 湿 | 沾色 | 褪色 | |
| 105 | 4~5 | 4~5 | 4 | 4 |
| 110 | 4~5 | 4~5 | 4 | 4 |
| 115 | 4~5 | 4~5 | 4 | 4~5 |
| 120 | 4~5 | 4~5 | 4 | 4~5 |
| 125 | 4~5 | 4~5 | 4 | 4 |
注:针织鞋材染色压力为24 MPa,染色时间为60 min,CO2流量为400 kg/h。
2.2 力学性能分析
鞋材在穿着过程中,常受到复杂的作用力,对物理性能要求较高。超临界CO2染色环境多为高温高压,在上染的同时可能会对纤维结构造成一定影响,因此,对染后鞋材进行力学性能测试十分重要。
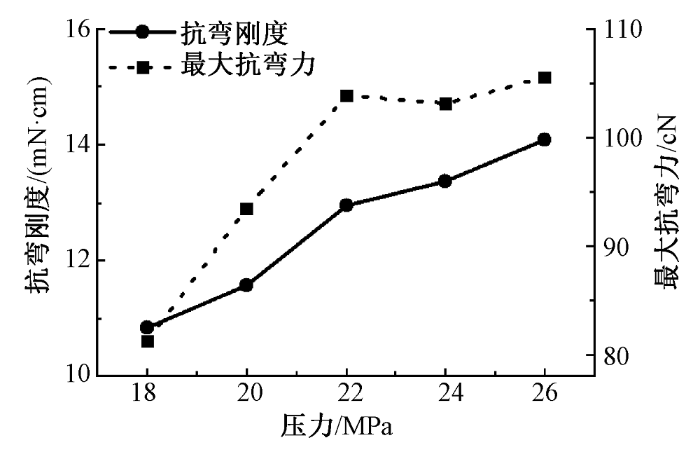
2.2.1 弯曲性能
图7
图7
压力对针织鞋材弯曲性能的影响
Fig.7
Influence of pressure on bending property of knitted shoe material
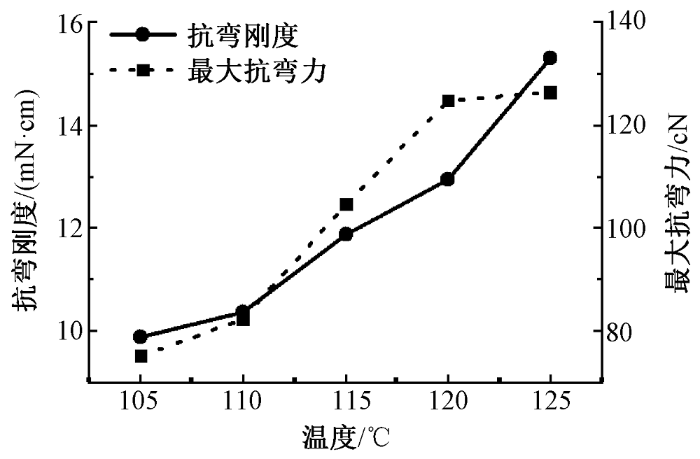
图8
图8
温度对针织鞋材弯曲性能的影响
Fig.8
Influence of temperature on bending property of knitted shoe material
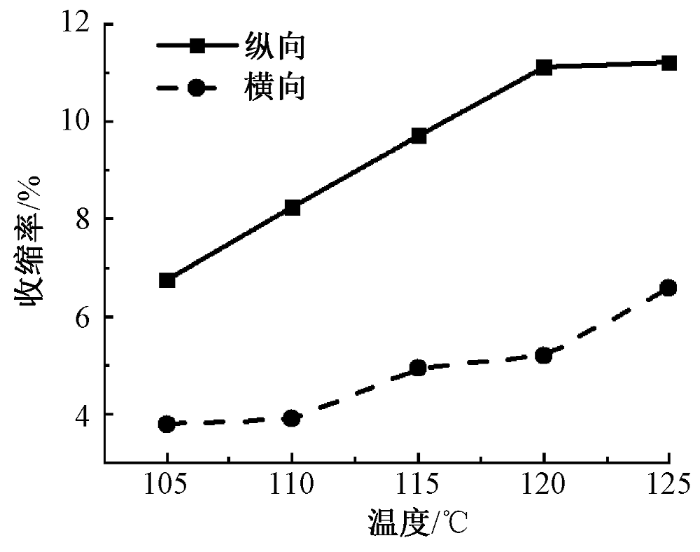
2.2.2 收缩性能
图9
图9
温度对针织鞋材收缩性能的影响
Fig.9
Influence of temperature on shrinkage of knitted shoe material
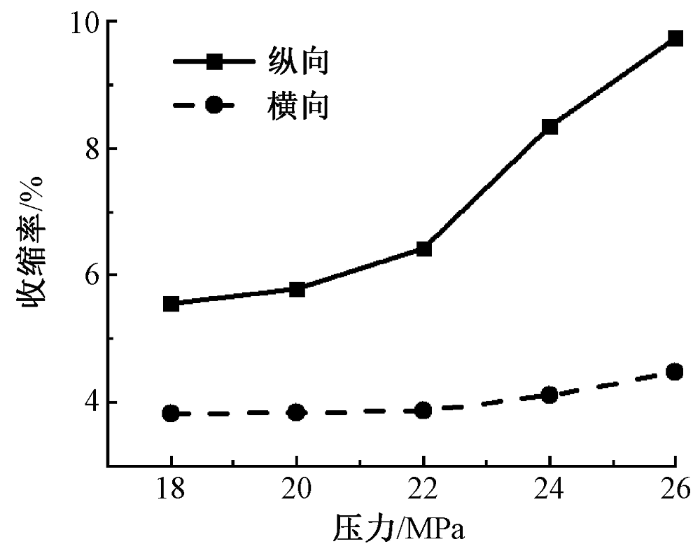
图10
图10
压力对针织鞋材收缩性能的影响
Fig.10
Influence of pressure on shrinkage of knitted shoe material
2.2.3 摩擦性能
表2 不同温度、压力下针织鞋材的摩擦因数
Tab.2
| 温度/ ℃ | 静摩擦 因数 | 动摩擦 因数 | 压力/ MPa | 静摩擦 因数 | 动摩擦 因数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 105 | 0.336 | 0.233 | 18 | 0.316 | 0.191 |
| 110 | 0.322 | 0.319 | 20 | 0.376 | 0.218 |
| 115 | 0.383 | 0.311 | 22 | 0.371 | 0.211 |
| 120 | 0.355 | 0.276 | 24 | 0.396 | 0.175 |
| 125 | 0.394 | 0.224 | 26 | 0.376 | 0.203 |
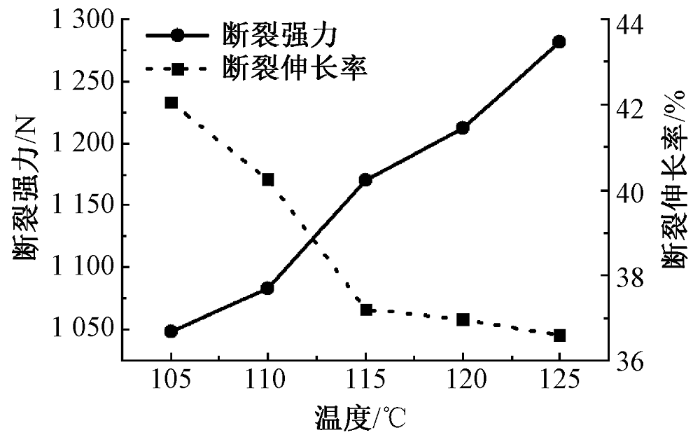
2.2.4 拉伸性能
图11
图11
温度对针织鞋材拉伸性能的影响
Fig.11
Influence of temperature on tensile property of knitted shoe material
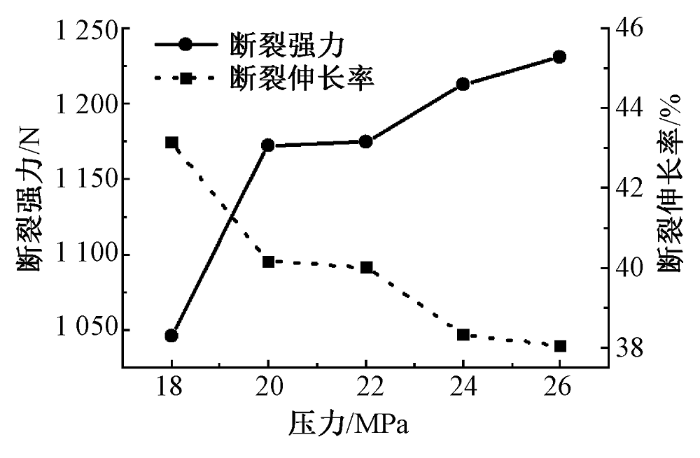
图12
图12
压力对拉伸性能的影响针织鞋材
Fig.12
Influence of pressure on tensile property of knitted shoe material
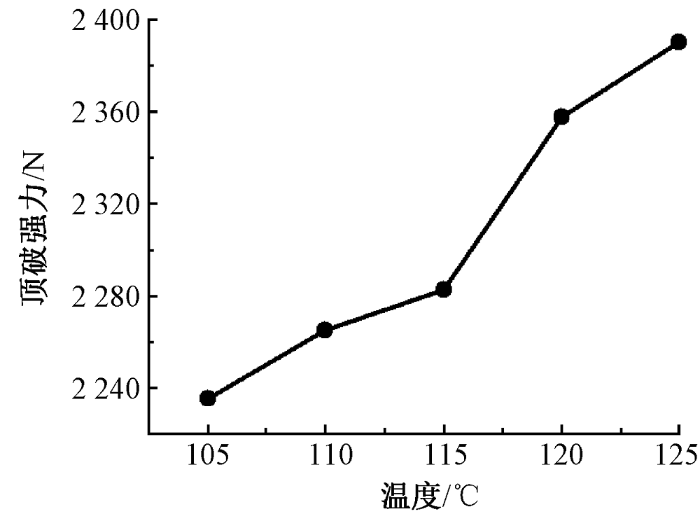
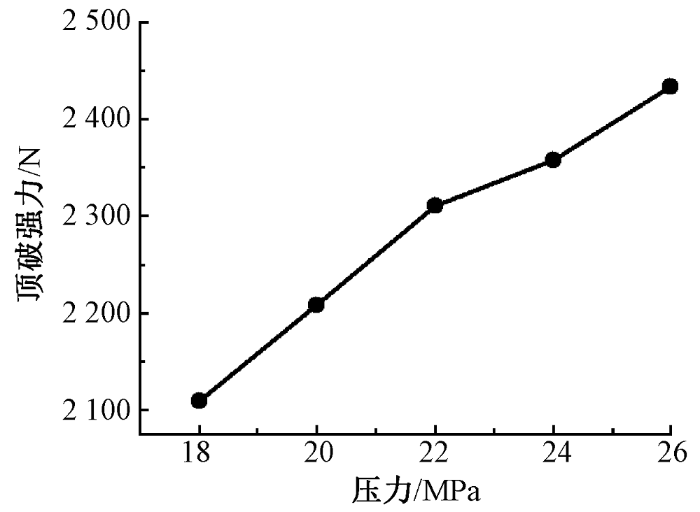
2.2.5 耐用性能
图13
图13
温度对针织鞋材耐用性能的影响
Fig.13
Influence of temperature on durability of knitted shoe material
图14
图14
压力对针织鞋材耐用性能的影响
Fig.14
Influence of pressure on durability of knitted shoe material
3 结论
本文使用自制的超临界CO2流体染色设备,研究了涤纶针织鞋材无水染色性能,进一步对超临界CO2染色后鞋材的力学性能进行了探究,得到如下结论:
1)染色压力、温度、时间对涤纶针织鞋材染色效果具有显著影响。涤纶针织鞋材超临界CO2无水染色最优工艺为:染色温度120 ℃,染色压力24 MPa,染色时间60 min。
2)超临界CO2无水染色可实现针织鞋材的均匀上染,色深偏差值稳定在0.1±0.05;耐皂洗色牢度达到4级以上,耐摩擦色牢度达到4~5级。
3)染色压力与染色温度对针织鞋材弯曲性能、收缩性能、拉伸性能以及耐用性能具有较大影响,对鞋材的摩擦性能基本无影响。
参考文献
横编成形鞋面的组织结构设计
[J].
Stitch structure design of flat knitting shaped shoe-upper
[J].
DOI:10.1177/004051756603600107
URL
[本文引用: 1]

Frictional contacts between crossing fibers consist of a true frictional component and a ratchet component that causes fiber migration. The saw-tooth shaped profile of a Merino wool fiber operates as a ratchet on the curved surface of crossing fibers up to a radius of curvature of the crossing fiber of about 50 microns: '
采用局部编制技术的毛衫特殊结构工艺与设计
[J].
Process and design of woolen sweater special structure based on partial technology
[J].DOI:10.1177/004051756703700106 URL [本文引用: 1]
CO2utilization for the dyeing of yak hair: fracture behavior in supercritical state
[J].
纺织染整领域支撑低碳排放的关键技术
[J].
Key technologies supporting low-carbon emissions in dyeing and finishing of textiles
[J].
An ecofriendly dyeing of wool with supercritical carbondioxide fluid
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.12.115 URL [本文引用: 1]
超临界流体染整技术研究进展
[J].
Research development of supercritical fluid dyeing and finishing technology
[J].
涤纶筒纱超临界二氧化碳流体染色工程化装备与工艺
[J].
Engineering plant and process for dyeing of polyester bobbins in supercritical CO2 fluid
[J].
分散染料在超临界二氧化碳流体中的溶解度
[J].
Study on solubility of disperse dyes in supercritical carbon dioxide fluid
[J].
Numerical simulation of CO2and dye separation for supercritical fluid in separator
[J].
涤纶织物在超临界二氧化碳中的染色性能研究
[J].
Study on the dyeing property of polyester fabric in supercritical carbon dioxide
[J].
C.I.分散棕19在超临界CO2及水中溶解性的分子动力学模拟
[J].
Molecular dynamics simulation of solubility of C.I. Disperse Brown 19 in supercritical CO2 and water
[J].
Phase equilibria of sulfoxide (DMSO) + carbon dioxide, and DMSO + carbon dioxide + water mixtures
[J].DOI:10.1016/j.supflu.2006.12.015 URL [本文引用: 1]
CO2 utilization for the waterless dyeing: characterization and properties of Disperse Red 167 in supercritical fluid
[J].
超临界二氧化碳无水工程化染色中羊毛纤维的力学性能
[J].
Mechanical properties of wool fibers in engineering anhydrous dyeing using supercritical carbon dioxide
[J].
超临界CO2中混合分散染料对涤纶织物的染色研究
[J].
Study on the dyeing of terylene fabric with mixed disperse dyes in supercritical carbon dioxide
[J].
Dye distribution in supercritical dyeing with carbon dioxide
[J].DOI:10.1016/S0896-8446(01)00102-4 URL [本文引用: 1]
活性分散黄染料对涤纶/棉混纺织物的超临界CO2同浴染色
[J].
One-bath dyeing of polyester/ cotton blended fabrics in supercritical CO2 with Reactive Disperse Yellow dye
[J].
超临界CO2在PLA纤维染色中的应用
[J].
Application of supercritical CO2 in dyeing polylatic acid fiber
[J].
涤纶针织物碱减量和染色一浴一步法工艺
[J].
Alkali reduction and one-bath-one-step process for dyeing polyester knitted fabric
[J].
超临界CO2流体处理对涤纶纤维结构的影响
[J].
Effect of supercritical CO2treatment on the structure of PET fiber
[J].
超临界二氧化碳对涤纶纤维结构和性能的影响
[J].
Effect of supercritical carbon dioxide on structure and properties of polyester fiber
[J].
Insituspectroscopy of polymers subjected to supercritical CO2: plasticization and dye impregnation
[J].
DOI:10.1366/0003702971940765
URL
[本文引用: 1]

In situ FT-IR spectroscopy has been used to study poly(methyl methacrylate) films subjected to high-pressure and supercritical CO2. Spectral changes indicate increased molecular mobility of ester groups due to the plasticization effect of CO2 on PMMA. This increase in PMMA segmental mobility has been used to impregnate Disperse Red 1 dye (DR1) into polymer film from a supercritical fluid solution. The enhanced diffusion process was observed in situ via FT-IR and UV/vis spectroscopy.
热定型温度对涤纶针织物性能的影响
[J].
Effects of heat setting temperature on the properties of knitted polyester fabrics
[J].
超临界二氧化碳处理对聚酯纤维结构及其性能的影响
[J].
Effect of supercritical carbon dioxide treatment on structure and properties of polyester fiber
[J].
超临界CO2处理温度对二醋酸纤维结构与性能的影响
[J].
Effect of supercritical CO2treatment temperature on structure and property of diacetate fiber
[J].
超临界CO2喷射中拉伸对涤纶结构和性能的影响
[J].
Effect of tension on the structures and properties of PET fiber during spray in supercritical carbon dioxide
[J].




 京公网安备11010502044800号
京公网安备11010502044800号