随着城市化和工业化的加速发展,空气污染已成为日益严重的环境问题,对人类健康构成了巨大威胁。除了常见的悬浮颗粒物外,新型冠状病毒、甲型流感、支原体肺炎等传染性疾病也对公共卫生安全带来了巨大挑战[1⇓-3]。传统的空气过滤技术在应对如PM1.0或更小颗粒物时往往过滤效率低且空气阻力大[4]。纳米纤维材料具有高孔隙率、良好的孔隙连通性和大比表面积等特性,在解决这些问题方面具有独特优势。此类材料的生产基于静电纺丝技术,能够精确控制纳米纤维的尺寸、结构和形态,所制成的空气过滤纳米纤维材料可针对特定污染物颗粒尺寸进行有效过滤,已应用于个人防护、灰尘与有毒物质过滤、室内空气净化以及医疗环境中病毒与细菌的过滤等领域。然而,随着对此类材料的需求不断增加,其规模化生产成为亟待解决的关键问题。为此,本文介绍了3种常用的静电纺空气过滤纳米纤维材料制备工艺,分析了不同结构、不同功能的空气过滤纳米纤维材料,并对规模化静电纺丝技术和相应的理论研究进行了系统概述,以期为采用静电纺丝技术制备空气过滤纳米纤维材料提供一些具有启迪意义的参考。
1 静电纺材料制备工艺
目前用于过滤领域的静电纺丝加工方式有3种,包括熔融静电纺丝法、溶液静电纺丝法和气流辅助法。
1.1 熔融静电纺丝法
聚丙烯(PP)、涤纶(PET)等热塑性聚合物由于易获得且价格低廉,被大量应用于熔融静电纺丝。熔融静电纺丝过程先用高温装置加热将聚合物熔融挤出,然后利用高压静电场对聚合物进行牵伸纺丝,这使其更安全和环保。由于装置结构复杂,易和高压电源装置互相影响产生静电干扰,从而造成纺丝电压不稳定,而且聚合物熔体具有一定黏度,其产品纤维直径较溶液静电纺丝更粗,一般为微米级[5]。通过调整生产工艺参数,比如降低熔体流量,改变熔体温度和加热周围的空气等,可获得更细的纳米纤维。穆晓绮[6]研究了熔融静电纺PP纤维的细化与成形机制,纺丝电压的增大和辅助加热温度的升高可大幅减小纤维直径。白洋[7]通过在PET中加入聚乙二醇降黏剂,调控工艺参数,增强了纤维的力学性能,并将纤维直径由初始的11 μm减至4.3 μm,材料孔径减小,分布变窄,在过滤领域有良好的应用前景。
1.2 溶液静电纺丝法
在空气过滤领域常用于溶液静电纺丝的聚合物原料及其特点与应用如表1所示。
表1 常用于溶液静电纺丝的原料及其特点与应用
Tab.1
| 聚合物原料 | 特点 | 应用 |
|---|---|---|
| 聚丙烯酸丁酯(PBA) | 良好的拉伸性能和耐热性 | 纳米纤维膜和过滤材料 |
| 聚乳酸(PLA) | 良好的生物降解性和生物相容性 | 医用纳米纤维材料和口罩等 |
| 聚酰胺(PA) | 优异的力学性能和耐磨性 | 耐磨、高强度的静电纺丝纤维材料 |
| 聚醚醚酮 (PEEK) | 耐化学腐蚀、耐高温性能良好 | 高温环境下的静电纺纤维材料,如空气过滤材料等 |
| 聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯(PMMA) | 良好的耐候性和光学性能 | 透明、光学性能优异的静电纺纤维材料 |
| 聚醚砜(PES) | 良好的化学稳定性和热稳定性 | 高温、耐化学腐蚀的静电纺纤维材料,如滤网、膜材料等 |
| 聚偏氟乙烯 (PVDF) | 良好的耐磨性、耐化学性和耐候性,优异的电气性能和耐高温性 | 高性能的空气过滤材料,如高效过滤器和膜材料等 |
| 聚乙烯醇 (PVA) | 良好的力学性能、耐磨性和耐化学性,同时易溶于水 | 在湿度较大的环境下使用的空气过滤材料,如湿式过滤器等 |
对于熔融静电纺丝法,目前由其制备的纤维直径较粗,如何进一步将纤维做得更细以提高过滤效率是其中的关键难题。采用溶液静电纺丝法制备的材料更加多样,功能调控容易,且直径更加可控,因此适合被用来进行更小直径的功能性纳米纤维材料的制备。与此同时,如何开发环保可靠的绿色溶剂体系,并进一步提高生产效率是溶液静电纺丝技术面临的挑战。
1.3 气流辅助法
气流辅助法是在传统静电纺丝过程中额外加上辅助的气流,通过气流场和静电场的耦合作用对纤维进行牵伸。齐庆欢等[10]提出了一种静电-气流接替牵伸低黏度高电导率聚丙烯腈(PAN)纤维射流的方法,在最优工艺参数下可获得平均直径为90.91 nm的PAN纳米纤维,断裂强度达7.24 MPa,是常规PAN纳米纤维材料的2倍。元苹平等[11]在现有气流辅助法的基础上,设计了一种气流雾化静电纺丝装置,纺丝液在喷丝孔喷出后,被双狭缝气流击碎成细小颗粒,这些颗粒在气流力和电场力的耦合作用下被牵伸成丝,并在接收板上沉积。在最优工艺下,PAN纤维的平均直径在196 nm左右,产量达4.5 g/h,在90 L/min风速下的过滤效率达80%以上。气流辅助法虽然能细化纤维直径,但是气流的引入可能会导致纤维形成时的拉伸和定向性不稳定,使得纤维的直径和形态难以控制,影响纤维的均匀性,所以如何控制气流、气压等参数保证纤维的稳定产出需要进一步研究。
2 结构性静电纺材料制备
一般而言,由单组分制得的纳米纤维直径分布集中,孔径分布较窄,对于小于孔径的微小颗粒,纳米纤维材料无法有效过滤。研究发现,构建具有粗细混杂的两相结构或者引入大孔隙的纳米纤维材料形成梯度结构,有利于降低最易穿透粒径,同时保持较低的过滤阻力。
2.1 粗糙表面结构研究
提升纤维的比表面积对于颗粒物的拦截至关重要,而通过掺杂特定物质,纳米纤维的表面可形成粗糙纹理,这显著增强了纳米纤维材料的颗粒物过滤效率。在这一过程中,无机驻极体的加入不仅增大了纳米纤维材料的比表面积,还通过静电效应主动吸附颗粒物,从而提高了过滤性能。通常用于静电纺丝的颗粒包括聚四氟乙烯(PTFE)[12⇓-14]、二氧化硅(SiO2)[13]、四氧化三铁(Fe3O4)[15]、钛酸钡(BaTiO3)[16]、二氧化钛(TiO2)[17]、氮化硅(Si3N4)[18]、金属有机骨架材料(Zif-8)[19]、勃姆石(Boehmite)[20]、羟基磷氟石(HAP)[21]、石墨烯(GO)、碳纳米管(CNT)、凹凸棒石(attapulgite)[22]等。
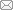
图1
图1
不同粗糙表面结构的纳米纤维材料表面扫描电镜照片
Fig.1
SEM images of nanofiber materials with different rough surface structures.
(a)rGO/PAN; (b)PI/SiO2; (c)PI/SiO2/ZIF-8; (d)NF/CNT; (e)F1-SAPAN
2.2 蜘蛛网结构研究
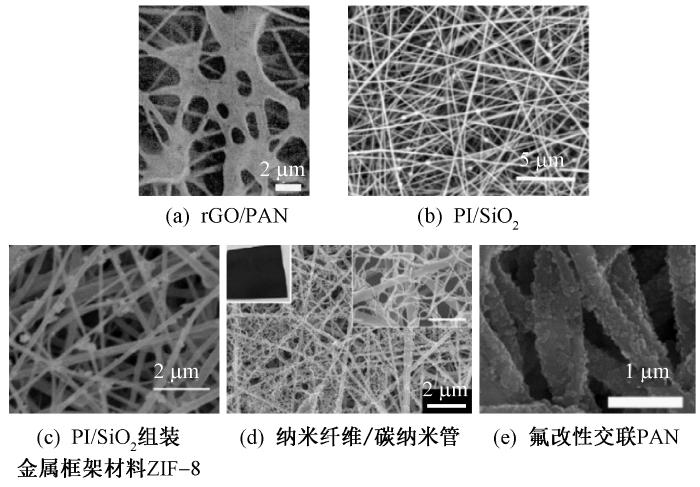
图2
图2
不同结构的纳米纤维材料表面扫描电镜照片
Fig.2
SEM images of nanofiber materials with different structures.
(a) Spider web structure; (b) Dendritic structure; (c) Groove structure; (d) Porous structure; (e) Multi-scale structure
2.3 树枝与沟槽结构研究
2.4 多尺度粗细纤维混杂结构研究
刘允璞等[34]利用新型无针式三喷头组合制备了PAN/PMMA双峰直径纳米纤维材料。利用梯度结构,增加材料的过滤效率,该材料的平均孔径为1.2 μm,过滤效率达99.93%,过滤阻力仅为124.46 Pa,品质因子为0.058 5 Pa-1,一定程度上达到了高效低阻。
2.5 串珠结构研究
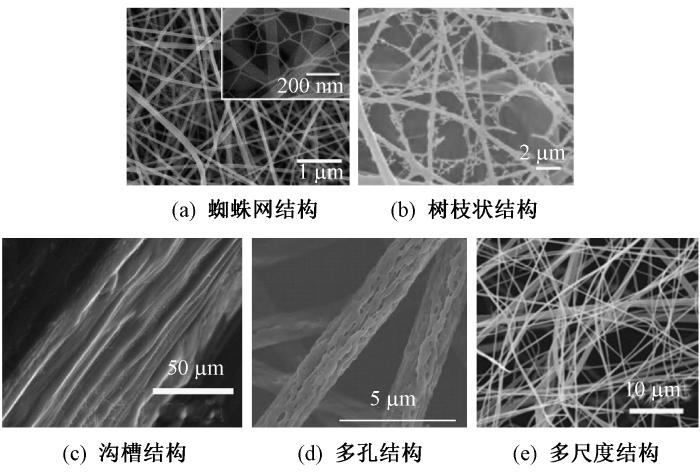
图3
图3
具有串珠与裂纹结构的纳米纤维材料表面扫描电镜照片
Fig.3
SEM images of nanofiber materials with beaded(a) and cracked(b) structures
总体来说,通过构建不同复杂结构的纳米纤维材料来增加比表面积,延长纳米纤维材料内部的气流流动通道,可有效增加颗粒物被捕捉的概率,提高过滤效率;大孔径的存在可保证较低的过滤阻力。目前复杂结构纳米纤维材料的加工过程较为繁琐,如何保证生产过程中的稳定高效,以及多级结构在长期或者循环使用过程中不被破坏,仍是需要研究的方向。
3 功能性静电纺材料制备
3.1 抗菌抗病毒材料制备
由于颗粒物中存在各种有机物、无机物及水分,给微生物的繁殖创造了有利条件,当其被纳米纤维材料拦截在表面和内部时,不及时清理会造成不良后果,纳米纤维材料的使用寿命和效果会大幅降低,同时会造成二次污染[36],因此,开发具有抗菌性能的纳米纤维材料有广阔的研究前景。
聚芳硫醚砜(PASS)是由聚苯硫醚(PPS)进行结构改性所得,与PPS相比,其玻璃化转变温度可达 220 ℃,热变形温度达190 ℃,具有更好的热稳定性和力学强度[37]。Su等[38]研究制备了PASS/Ag/ZnO复合纳米纤维材料,该材料表现出优异的力学性能、疏水性能和抗菌性能。在风速为50 cm/s和200 cm/s时,该材料对PM2.5的过滤效率分别达到99.41%和99.89%,同时分别仅产生42 Pa和79 Pa的过滤压降。Victor等[39]将PVDF与钛纳米管(TNT)进行混合静电纺丝,制得的PVDF/15% TNT纳米纤维材料的细菌过滤效率达99.88%,可用作口罩的除菌高效纳米纤维材料。为制备高效低阻空气过滤纳米纤维材料,Wang等[40]采用静电纺丝技术结合冷冻干燥的方法,将细菌纤维素纳米纤维、SiO2纳米纤维和疏水性Si—O—Si弹性黏合剂构建成笼状结构的超柔性纳米纤维气凝胶(CSA)。随后,通过N-卤胺化合物二羟甲基-5,5-二甲基乙内酰脲修饰,赋予了其病原体灭活功能。Jang等[41]采用静电纺丝技术在PVDF纤维中引入金属有机框架(MOFs)和Cu2O纳米颗粒。MOF是一种具有三维网络结构的微孔材料,具有良好的分散性、高比表面积和易于功能化的特点。与CuO以及诸如TiO2、ZnO、NiO等大多数金属氧化物相比,Cu2O纳米颗粒具有更强的抗菌能力。将MOFs和Cu2O引入PVDF纳米纤维材料中,能够高效去除空气中的颗粒物和细菌。
Shen等[42]提出了小分子牵引聚合物链,阳离子促进增强射流分裂机制,采用一步绿色静电纺丝法制备了具有双峰结构的玉米醇溶蛋白(Zein)/壳聚糖盐酸盐(CS)/根皮素(PL)全生物基纳米纤维材料。在溶液中,PL小分子分散并与聚合物链相互作用。研究结果显示,Zein/1CS/3PL材料具有出色的空气过滤性能,其空气过滤效率达到99.65%,压降仅为57.7 Pa,品质因子达到0.098 Pa-1,比N95高出63.3%。同时,基于PL和CS的协同抗菌机制,Zein/1CS/3PL材料表现出高效的抗菌性能,对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌的抑制率均达到99.9%。经过30 d测试,其抗菌性能仍然较高,对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌的抑制率分别为99.9%和98.1%。
Shen等[43]使用一种延迟挥发的绿色溶液体系,通过一步静电纺丝技术制备了优化结构的玉米醇溶蛋白/肉桂醛(CMA)复合纳米纤维材料。CMA的添加延迟了喷嘴堵塞时间,改善了纤维形态,并提高了纤维的疏水性和抗菌性能,从而增强了材料的空气过滤稳定性。此方法一定程度上缓解了喷嘴的堵塞时间,提高了制备效率,值得借鉴。
3.2 耐高温材料制备
工业的发展使得工业废气成为了空气污染的主要源头之一,耐高温的高效低阻过滤器成为重要发展方向。郭朝阳等[44]通过添加表面活性剂,制备了新型聚醚酰胺纳米纤维材料,该材料平均孔径为2.8 μm,对PM0.3的过滤效率为98.37%,并具有良好的耐高低温、耐酸碱性能,在化工厂和燃煤电厂等高温、酸性条件下具有性能优势。芳纶同样在高温防护、工业过滤等方面应用广泛,Yu等[45]制备了聚间苯二甲酰间苯二胺(PMIA)纳米纤维材料,其过滤效率在99.9%左右,但其压降高达466.6 Pa。Wu等[46]利用静电纺丝成功制备PES/MOF纳米纤维材料,其直径为(1.22±0.55) μm,具有优异的力学性能和高过滤效率,所得材料PES/MOF-0.075表现出优异的过滤效率,对直径为0.225~0.4 μm颗粒的过滤效率超过99.3%,对氯化钠颗粒的过滤压降为57 Pa。Kang等[47]在350 ℃的空气中进行PAN/聚乙烯吡咯烷酮(PVP)/SnO2纳米纤维材料的热诱导环化和氧化反应。在热氧化过程中,Sn2+充当催化剂和活化剂,有效地阻止了PAN纳米纤维的熔融和融合;PVP的加入显著提升了纳米纤维材料的力学性能。该纳米纤维材料在室温下表现出卓越的PM过滤性能,对PM0.3和PM2.5的过滤效率分别达到了99.53%和99.98%。
4 静电纺材料规模化制备
随着对静电纺材料需求的不断增加,其规模化生产成为亟待解决的关键问题。Liu等[48]定义了描述液滴-射流形状的3个参数(针头液滴曲率、初始射流直径和过渡斜率),并探究了这些形状参数与纤维直径之间的关系。随着形状参数的增大,纤维直径也随之增大,此外,初始射流直径与纤维直径之间的关系以及过渡斜率与纤维直径之间的关系不受施加电压和聚合物溶液浓度的影响,但液滴-射流形状必须保持稳定。周智勇[49]通过有限元模拟及实验验证,推导出了高压电场环境中喷头曲率与电场强度、边缘电荷密度的关系,并设计出高曲率圆边碟形喷头,增强边缘电场强度,获得了更细的纳米纤维。Xiong等[50]通过构建一种蘑菇状静电纺丝装置,获得了高曲率的稳定环形预泰勒锥,这些预泰勒锥可将表面电荷均匀地控制在射流激发的位置,通过控制PTFE覆盖表面的尺寸来控制泰勒锥曲率的大小。覆盖表面的纺丝液表面电荷分布均匀,电荷密度较高,相比于未覆盖表面的相同装置,在同等纺丝条件下,蘑菇状纺丝头表现出优异的浓缩电荷能力,有效地降低了形成泰勒锥射流的临界电压,在相同电压下,射流数明显增多。最终制得的材料直径分布变异系数为10%,产能为13.7 g/h,表现优异。
Lei等[51]研究了射流拉伸控制成形纤维直径机制,建立了通过控制摆动射流速度控制纤维直径的模型。在溶液中加入LiCl,增加了纺丝液的电导率,在纺丝过程中,大量的自由电荷被转移到旋转射流的表面,导致射流在电场中的速度增加,纤维细度得以减小。制得的0.521 g/m2的纳米纤维材料对小于0.26 μm的NaCl气溶胶颗粒的过滤效率达99.93%,压降低至105.2 Pa。
在此基础上,权震震等[52]建立了多曲面喷头静电纺丝理论,证明了多曲面正电极在临界电压下可同时产生多股射流,纺丝效率大幅提升,产量是传统单针头的1 000倍,大幅提高了生产效率,为批量产业化制造纳米纤维提供了理论参考。
然而,面对目前极大的需求,静电纺纳米纤维的宏量制备虽已有实质性提高,但仍需进一步开发大规模制备的先进技术,明晰多射流制备过程中射流间的相互作用,控制多射流的鞭动状态对于高质量的规模化纳米纤维生产具有重要意义。
5 结束语
静电纺丝可制得高效、低阻、高强的纳米纤维材料,同时可赋予其抗菌、耐高温等特性。近年来,纳米纤维材料特殊结构的构建与新型材料的研究为多功能空气过滤材料提供了新方法,但也同样有许多不足:1)目前,静电纺纳米纤维材料的再生和重复使用能力有限,这可能导致较高的长期运营成本;2)静电纺纳米纤维材料的力学强度通常较低,容易受到物理损伤,目前还都是与其它材料进行复合使用,限制了其在某些应用中的耐用性;3)静电纺丝的规模化生产仍面临挑战,为进一步提高产量,需要对宏量制备过程中多射流间的协同控制机制进行进一步研究。
基于上述问题,需要进一步深入研究静电纺丝机制,探究电场、溶液、纤维成形之间的影响机制与构效关系,以及对纤维形态和材料结构的精确控制,从而开发新技术来实现高效稳定的规模化生产。同时研发具备自清洁、抗菌和传感等功能的纳米纤维材料,以提高其在空气过滤领域的应用价值。此外,结合新型纳米纤维材料和纤维功能改性技术,可进一步拓展静电纺纳米纤维材料的应用领域。随着技术的不断创新和研究的深入,静电纺纳米纤维材料在空气过滤领域的潜力将得到更充分的发挥和应用。
参考文献
The emergence, genomic diversity and global spread of SA-RS-CoV-2
[J].
SARS-CoV-2 infection induces long-lived bone marrow plasma cells in humans
[J].
Reduced sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 variant Delta to antibody neutralization
[J].
Electrospinning and electrospun nanofibers: methods, materials, and applications
[J].
DOI:10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00593
PMID:30916938
[本文引用: 1]

Electrospinning is a versatile and viable technique for generating ultrathin fibers. Remarkable progress has been made with regard to the development of electrospinning methods and engineering of electrospun nanofibers to suit or enable various applications. We aim to provide a comprehensive overview of electrospinning, including the principle, methods, materials, and applications. We begin with a brief introduction to the early history of electrospinning, followed by discussion of its principle and typical apparatus. We then discuss its renaissance over the past two decades as a powerful technology for the production of nanofibers with diversified compositions, structures, and properties. Afterward, we discuss the applications of electrospun nanofibers, including their use as "smart" mats, filtration membranes, catalytic supports, energy harvesting/conversion/storage components, and photonic and electronic devices, as well as biomedical scaffolds. We highlight the most relevant and recent advances related to the applications of electrospun nanofibers by focusing on the most representative examples. We also offer perspectives on the challenges, opportunities, and new directions for future development. At the end, we discuss approaches to the scale-up production of electrospun nanofibers and briefly discuss various types of commercial products based on electrospun nanofibers that have found widespread use in our everyday life.
静电纺丝纳米纤维制备技术应用研究进展
[J].
Research progress of electrospinning nanofiber preparation technology
[J].
静电纺芳纶纳米纤维膜的制备及其过滤性能
[J].
DOI:10.19398/j.att.202206047
[本文引用: 1]

为获得高效低阻的过滤材料,以间位芳纶为原料,采用静电纺丝的方法,通过对纺丝溶液和纺丝工艺的优化制备芳纶纳米纤维空气过滤材料,并研究纳米纤维的形貌和直径、纳米纤维膜的过滤性能和热稳定性能。结果表明:当纺丝溶液溶质的质量浓度为8%、纺丝电压20 kV、进液流量0.3 mL/h、接收距离15 cm时,可制备得到纤维平均直径约为50 nm的纳米芳纶纤维过滤材料;当纺丝时间为5 h时,其过滤效率可达到99.5%,阻力仅为123.8 Pa,去除静电处理后过滤效率依然可以达到89.4%。此外,制备的芳纶纳米纤维过滤材料具有优良的热稳定性和尺寸稳定性,在耐高温高效过滤领域具有应用前景。
Preparation and filtration performance of aramid nanofiber membrane by electrostatic spinning
[J].
DOI:10.19398/j.att.202206047
[本文引用: 1]

Meta aramid (PMIA) is a kind of high-performance fiber, which has many excellent properties such as high strength, high modulus, high temperature resistance, chemical corrosion resistance, dimensional stability and so on. It is widely used in the fields of high temperature protection, industrial filtration and new energy. With the research and development of nanofiber technology, PMIA nanofibers have received extensive attention in the filtration field due to their high specific surface area, micro effects, interface effects and many other characteristics. Electrospinning is one of the common methods to prepare nanofibers and it has the advantages of low cost, simple operation and continuous preparation of controllable nanofibers. At present, researchers have studied the basic conditions of PMIA dissolution and electrospinning process respectively, and prepared nanofiber filter membranes with high filtration efficiency by using special technologies such as electrostatic spray screen. However, there are problems such as relatively large average diameter of nanofibers, decreased filtration efficiency of nanofiber membranes, large pressure drop, high equipment requirements and complex process.<br/>Firstly, we explored the influence of electrospinning process parameters, such as the concentration of solute in spinning solution, electrospinning voltage, feed flow rate and collection distance on the diameter and morphology of nanofibers, obtaining the optimal process parameters. Secondly, we explored the influence of the spinning time on the filtration performance of composite filter materials by controlling the spinning time so that nanofiber filter membranes with different thicknesses could be formed on the substrate. Thirdly, we compared the changing rule of the filtration performance of the electrostatic filter materials whose static electricity is eliminated by isopropanol vapor with that of the filter materials without eliminating static electricity. Finally, the thermal dimensional stability and thermogravimetric stability of electrospun filter materials were studied and analyzed. By controlling and optimizing the morphology of PMIA nanofibers, filter materials with high efficiency and low resistance could be obtained. The results show that when the spinning solution concentration is 8%, the spinning voltage is 20 kV, the feeding speed is 0.3 mL/h, and the receiving distance is 15 cm, the average diameter of the obtained nanofibers is small, the fibers are smooth and regular, and the morphology is good. When the spinning time is 5 h, the filtration efficiency of the nanospun membrane for NaCl aerogel particles with median particle size of 0.26 μm reaches 99.5%, and the resistance is only 123.8 Pa. After electrostatic treatment, the filtration efficiency can still reach 89.4%; the size of the nanofiber membrane is basically unchanged in the temperature range of below 290 ℃, and the thermal weight loss at 400 ℃ is only 5%.<br/>The electrospun PMIA nanofiber filter material has good filtration performance, dimensional stability and high temperature resistance, and is easy to be prepared on a large scale. It has an important application prospect in the field of high temperature and high efficiency filtration.
Biodegradable Electroactive nanofibrous air filters for long-term respiratory healthcare and self-powered monitoring
[J].
静电—气流接替牵伸纺制PAN亚百纳米纤维及参数探讨
[J].
Study on the parameters of PAN nanofibers produced by electrostatic-pneumatic replacement drafting
[J].
基于气流雾化静电纺纳米纤维的制备及其空气过滤性能
[J].
Preparation and air filtration performance of nanofibers based on air atomization electrostatic spinning
[J].
Electret polyvinylidene fluoride nanofibers hybridized by polytetrafluoroethylene nanoparticles for high-efficiency air filtration
[J].
Electrospun-SiO2-nanofiber-reinforced cellulose aerogel loaded with ZIF-67 for air filtration and formaldehyde adsorption
[J].
High efficiency, low resistance and high temperature resistance PTFE porous fibrous membrane for air filtration
[J].
Characterization of electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride-loaded iron sand based Fe3O4 nanoparticles
[J].
High-performance electrospun particulate matter (PM) filters embedded with self-polarizable te-tragonal BaTiO3 nanoparticles
[J].
Fabrication and characterization of multifunctional nanoclay and TiO2embedded polyamide electrospun nanofibers and their applications at indoor air filtration
[J].
静电驻极PVDF-TiO2/Si3N4纳米纤维膜的制备及其空气过滤性能
[J].
Preparation and air filtration performance of electrostatic electret PVDF-TiO2/Si3N4 nanofiber membranes
[J].
Zeolite imidazole frame-work-8(ZIF-8) decorated keratin-based air filters with formaldehyde removal and photocatalytic disinfection performance
[J].
Laminated polyacrylonitrile nanofiber membrane codoped with boehmite nanoparticles for efficient electrostatic capture of particulate matters
[J].
Ultrafine, self-crimp, and electret nano-wool for low-resistance and high-efficiency protective filter media against PM0.3
[J].
DOI:S0021-9797(20)30742-6
PMID:32544628
[本文引用: 1]

Frequent outbreaks of emerging infectious diseases (EIDs) make personal protective filter media in high demand. Electrospun nanofibrous materials are proved to be very effective in resisting virus-containing fine particles owing to their small fiber diameters; however, hindered by the intrinsic close-packing character of fine fibers, electrospun filters suffer from a relatively high air resistance, thereby poor breathing comfort. Here, we report a biomimetic and one-step strategy to create ultrafine and curly wool-like nanofibers, named nano-wool, which exhibit fluffy assembly architecture and powerful electret effect. By achieving the online self-crimp and in-situ charging of nanofibers, the curly electret nano-wool shows a small diameter of ~0.6 μm (two orders of magnitude lower than natural wool: ~20 μm) and an ultrahigh porosity of 98.7% simultaneously, together with an ultrahigh surface potential of 13260 V (one order of magnitude higher than previous filters). The structural advantages and powerful electret effect enable nano-wool to show excellent filtration efficacy (>99.995% for PM) and low air resistance (55 Pa). Additionally, nano-wool can be easily scaled up, not only holding great industrial prospect in personal protective respirators, but also paving the way for developing next-generation wool in a cost-efficient and multifunctional form.Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
The preparation of bifunctional electrospun air filtration membranes by introducing attapulgite for the efficient capturing of ultrafine PMs and hazardous heavy metalions
[J].
Multiscale nanoarchitectured fibrous networks for high-performance, self-sterilization, and recyclable face masks
[J].
Tailoring mechanically robust poly(m-phenylene isophthalamide) nanofiber/nets for ultrathin high-efficiency air filter
[J].
静电纺树枝状聚乳酸纳米纤维膜的制备及其过滤性能
[J].
DOI:10.13475/j.fzxb.20180801206
[本文引用: 1]

为开发可用于空气过滤的纳米纤维,利用静电纺丝技术一步法制备了树枝状聚乳酸(PLA)纳米纤维膜,探讨了溶剂种类、四丁基氯化铵(TBAC)添加量和纺丝电压对纤维膜形貌结构和性能的影响,同时研究了TBAC 添加量和纤维膜厚度对纤维膜过滤效果的影响。结果表明:溶剂为二氯甲烷,PLA 和TBAC 质量比为8:1,纺丝电压为30 kV 时,制得的纤维膜树枝状结构最为明显,其断裂应力和品质因数分别为23 MPa 和0. 068,优于纯PLA 纤维膜的5 MPa 和0. 059;随TBAC 质量分数的增加,纤维膜的接触角由118°降低至54. 5°;当具有明显树枝状结构的纤维膜厚度从10 μm 增加至40 μm 时,过滤效率和压降均增大,且当膜厚度为20 μm 时,过滤效率达到99. 89%,阻力约为96. 08 Pa,可满足高效空气过滤需求。
Preparation and filtration properties of electrospun dendritic polylactic acid nanofiber membranes
[J].
DOI:10.13475/j.fzxb.20180801206
[本文引用: 1]

In order to develop nanofibers with efficient air filtration performance, polylactic acid (PLA) tree-like nanofiber membranes were prepared by electrospinning. The effects of solvent type, addition amount of tetrabutylammonium chloride (TBAC) and spinning voltage on the morphology and properties of fiber membranes were investigated. In addition, the effect of TBAC addition and fiber membrane thickness on filtration efficiency was also studied. The results show that when the solvent is dichloromethane, the PLA/ TBAC mass ratio is 8 ∶ 1, and the spinning voltage is 30 kV, the fiber membrane has obvious tree-like structure. The fracture stress and quality factor of fiber membrane with obvious tree-like structure are 23 MPa and 0. 068, respectively, which is higher than 5 MPa and 0. 059 of the pure PLA fiber membrane. With the increase of the TBAC content, the contact angle of fiber membrane decreases from 118° to 54. 5°. For PLA nanofiber membranes with distinct tree-like structure, when the thickness of the fiber membrane increases from 10 μm to 40 μm, both filtration efficiency and pressure drop increase, especially, when the film thickness is 20 μm, the filtration efficiency of the fiber membrane is 99. 89%, and the resistance is about 96. 08 Pa, which can meet the demand for efficient air filtration.
Dual-bionic, fluffy, and flame resistant polyamide-imide ultrafine fibers for high-temperature air filtration
[J].
静电纺聚乳酸纳米纤维的制备及其孔结构调控
[J].
DOI:10.19491/j.issn.1001-9278.2023.04.011
[本文引用: 1]

为了调控聚乳酸(PLA)纳米纤维的孔结构,采用静电纺丝技术,以PLA母粒为原料,三氯甲烷(CF)和N,N⁃二甲基甲酰胺(DMF)按一定比例混合的溶液为溶剂,制备了平均直径在1.37 μm的PLA纳米纤维,并对其结构进行表征。结果表明,PLA纳米纤维的平均直径随着纺丝液中CF含量、聚合物浓度、环境湿度的增加而增大;随纺丝电压和灌注速度的增大而呈减小的趋势。同时,环境湿度对纤维表面孔结构有显著影响。随着湿度的增加,纤维表面孔的分布密度增加,且形状由圆形转变为椭圆形。此外,与表面光滑的PLA纳米纤维(2.4 m<sup>2</sup>/g)相比,所制备的PLA多孔纤维的比表面积提升了10倍(24.0 m<sup>2</sup>/g)。
Preparation and pore structure control of polylactic acid nanofibers by electrostatic spinning
[J].
DOI:10.19491/j.issn.1001-9278.2023.04.011
[本文引用: 1]

To regulate the pore structure of poly(lactic acid) (PLA) nanofibers, the nanofibers with an average diameter of 1.37 μm were prepared through electrospinning using PLA masterbatch as a raw material and the chloroform (CF)/N, N⁃dimethylformamide solution as a solvent, and their structures were investigated. The results indicated that the average diameter of the resultant nanofibers increased with an increase in the CF content, polymer concentration, and ambient humidity. With improving the spinning voltage and the filling speed, the average diameter tended to decrease. Meanwhile, environmental humidity has a significant effect on the pore structure of the fiber surface. The distribution density of pores on the fiber surface increased with an increase in humidity, and the shape varied from round to oval. In addition, the specific surface area of the as⁃prepared porous fiber was increased by 10 times (24.0 m2/g) compared to that of the PLA nanofibers with a smooth surface (2.4 m2/g).
High-performance antihaze window screen based on multiscale structured polyvinylidene fluoride nanofibers
[J].
空气过滤用复合纳米纤维膜的制备及其性能
[J].
Preparation and properties of composite nanofiber membrane for air filtration
[J].
Building bimodal structures by a wettability difference-driven strategy for high-performance protein air-filters
[J].
空气过滤微纳米纤维膜的组合式制备及其性能
[J].
Composite preparation and properties of micro-nano fiber membrane for air filtration
[J].
Multi-level structured polylactic acid electrospunfiber membrane based on green solvents for high-performance air filtration
[J].
空气过滤用纳米纤维膜研究进展
[J].
Research progress of nanofiber membrane for air filtration
[J].
Highperformance filter membrane composed of oxidized poly (arylene sulfide sulfone) nanofibers for the highefficiency air filtration
[J].
Electrospun composite membrane based on polyarylene sulfide sulfone/Ag/ZnO nanofibers for antibacterial effective PM2.5 filtration
[J].
Electrospun nanofibers of polyvinylidene fluoride incorporated with titanium nanotubes for purifying air with bacterial contamination
[J].
Tailoring nanonets-engineered superflexible nanofibrous aerogels with hierarchical cage-like architecture enables renewable antimicrobial air filtration
[J].
Preparation and characterization of multifunctional nanofibers containing metal-organic frameworks and Cu2O nanoparticles: particulate matter capture and antibacterial activity
[J].
Fully bio-based zein/chitosan hydrochloride/phloretin bimodal fibrous membrane for high-performance and antibacterial air filtration based on green electrospinning
[J].
Biobased nanofibrous membrane via delayed-volatilizing green electrospinning for high-performance air filtration
[J].
静电纺聚醚酰胺纳米纤维膜的制备及其空气过滤性能
[J].
Preparation of polyetheramide nanofiber membrane by electrostatic spinning and its air filtration perfor-mance
[J].
Preparation and characterization of PMIA nanofiber filter membrane for air filter
[J].
Electrospun polyethersulfone@MOF composite membranes for air cleaning and oilwater separation
[J].
Efficient removal of high-temperature particulate matters via a heat resistant and flame retardant thermallyoxidized PAN/PVP/SnO2 nanofiber membrane
[J].
Droplet-jet shape parameters predict electrospun polymer nanofiber diameter
[J].
DOI:10.1016/j.polymer.2019.01.082
[本文引用: 1]

Correlations between observable features of the droplet-jet shape and the diameter of electrospun nanofiber were studied. Three shape parameters derived from optical images of the jet transforming from a droplet were identified. They are "L-R curvature", "initial jet diameter", and "transition slope". Nanofiber diameter increased as the observed value of each shape parameter increased. The correlation between "initial jet diameter" and fiber diameter, as well as the correlation between "transition slope" and fiber diameter, were not affected by the variation of voltage or concentration of the polymer solution. "Initial jet diameter" and "transition slope" have potential applications in online controlled electrospinning to predict nanofiber diameter as real-time feedback information to guide the control of electrospun nanofiber diameter.
Mass production of high-quality nanofibers via constructing pre-Taylor cones with high curvature on needleless electrospinning
[J].
Controllable diameter of electrospun nanofibers based on the velocity of whipping jets for high-efficiency air filtration
[J].



 京公网安备11010502044800号
京公网安备11010502044800号