随着 “双碳”战略的实施,纺织行业坚持以绿色发展为导向,传统石油基纤维已不能满足人们现阶段对环保健康生活的要求。以植物为来源的纤维素纤维具有可再生、可降解以及良好的生物相容性[1-2],被广泛应用于纺织服装、生物医学、食品包装和智能材料等领域[3⇓-5]。纤维素纤维一直是制备柔性材料的理想基材,其内部强烈的分子间和分子内氢键使之具有较高的力学强度和高结晶度[6]。另外,纤维素分子链上大量的羟基活性位点可与多种官能团进行酯化[7]、醚化[8]和接枝共聚[9]等多类型反应,从而表现出优越的化学和物理性能。尽管纤维素纤维在生活中得到广泛应用,但自身的易燃属性严重限制了其在阻燃领域(阻燃防护服、汽车内饰、家居用品等)的实际运用和发展。
目前,提高纤维阻燃性能的方法多种多样,主要分为2类:一种是在纤维表面进行改性处理,如:构建阻燃涂层[10]、化学接枝[11]、浸渍固化[12]、静电自组装[13]等方法。表面改性处理通常对纤维内部结构影响较小,能较好地保持纤维力学强度,但往往反应条件苛刻,操作复杂,规模化制备要求高,且表面涂层与基体材料之间的界面结合力对阻燃耐久性起到至关重要的作用[14];另一种方法是在纤维成形前将阻燃剂等功能组分通过共混的方式加入纺丝液或熔体中进行纺丝,常见的阻燃添加剂有磷系[15]、氮系[16]、硅系[17]和金属氢氧化物[18]等。共混法制备阻燃纤维操作简单,是常用的阻燃改性手段之一,特别是在阻燃粘胶纤维的制备领域被广泛使用,但阻燃剂与基体材料之间的相容性需重点关注。阻燃剂颗粒过大,可能会造成加工困难、制品力学性能下降等问题。此外,已有多种化学或物理导电方法被用来对非导电纤维素纤维进行改性,如气相沉积、喷涂、自组装等,但往往存在界面结合力弱,操作成本高昂等问题;而水凝胶纤维具有良好的离子导电性、柔韧性和生物相容性等特点,在可穿戴电子设备和智能传感领域应用颇广。综上,阻燃性和力学强度之间难以调和的矛盾以及日益突出的多功能性需求,是纤维素纤维今后发展面临的挑战。
1 实验部分
1.1 实验材料
莱赛尔纤维(Lyocell,线密度为1.3 dtex),山东英利实业有限公司;氯乙酸(MCA,纯度99%),上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司;氢氧化钠(NaOH,纯度≥96%)、乙醇(EtOH,纯度95%),国药集团化学试剂有限公司;去离子水,实验室自制。
1.2 样品制备
将氯乙酸和氢氧化钠按照一定比例置于 100 mL 乙醇溶液中,在磁力搅拌器(上海力辰仪器科技有限公司)上于室温下搅拌1 h,直至完全溶解。将莱赛尔纤维清洁干燥处理后放入氯乙酸酒精溶液中,缓慢搅拌反应2 h。待反应结束后取出纤维,用70%的酒精溶液浸泡清洗3次以上,以去除纤维表面残留杂质。在烘箱(60 ℃)中干燥30 min,得到具有高吸水性的羧甲基化莱赛尔纤维(Lyocell-Na),其吸水后得到纤维素基水凝胶纤维。
1.3 测试与表征
1.3.1 形貌观察
采用Quanta250 FEG型场发射扫描电子显微镜(美国FEI公司)对改性前后的纤维表面进行形貌表征。测试前,采用离子溅射仪对样品进行喷金处理(120 s),测试电压为10 kV。
1.3.2 化学结构表征
采用Nicolet 5700型FT-IR光谱仪测试样品的傅里叶变换红外光谱,分析样品的化学结构。扫描范围为4 000~400 cm-1。
1.3.3 热稳定性测试
热重分析(TGA)使用SDT Q600型热分析仪(美国TA 仪器公司)进行。氮气气氛,氮气流量为50 mL/min, 从30 ℃升温到700 ℃,线性升温速率为10 ℃/min。
1.3.4 极限氧指数测试
采用HC-2C型氧指数仪(南京江宁仪器分析有限公司)测试纤维的极限氧指数。测试前对纤维进行编织处理,以固定纤维形状。
1.3.5 燃烧性能测试
参照ASTM D7309—2013《用微型燃烧量热法测定塑料和其他固体材料易燃性特性的标准试验规范》,采用PCFC型微型量热计(英国FTT公司)测试纤维的燃烧性能,记录样品真实燃烧过程中的热释放速率、总热释放量等数据。
1.3.6 力学性能测试
参照GB/T 14337—2022《化学纤维 短纤维拉伸性能试验方法》,采用Favimat-airobot型自动单纤维测试仪(德国TEXTECHNO公司)对单根纤维进行拉伸强度测试。试样间隔为20 mm,拉伸速度为10 mm/min。
1.3.7 传感性能测试
将纤维采用编织的方式制成测试样条,两端采用铜线固定并充当电极。采用CHI760E型电化学工作站(上海辰华仪器有限公司)在室温下记录电流信号的变化,进行传感性能测试。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 纤维微观形貌分析
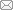
原始莱赛尔纤维和羧甲基化改性后的纤维表面形貌如图1所示。可以看出,纤维改性前后表面无明显差别,均呈光滑平直形貌,且未产生原纤化现象。从纤维直径来看,改性前莱赛尔纤维的直径约为10.3 μm,但改性后纤维直径略有增加(约为11.6 μm),这可能是由于反应过程是在碱性环境中进行,NaOH进入到纤维中的部分无定形区,使得纤维发生轻微润胀。该实验条件下的醚化反应不会对纤维造成过度损伤,反应过程相对温和,有利于较好地保持原始纤维的形貌和力学强度。
图1
图1
莱赛尔纤维羧甲基化改性前后的扫描电镜照片
Fig.1
SEM images of Lyocell fiber before (a) and after (b) carboxymethylation modification
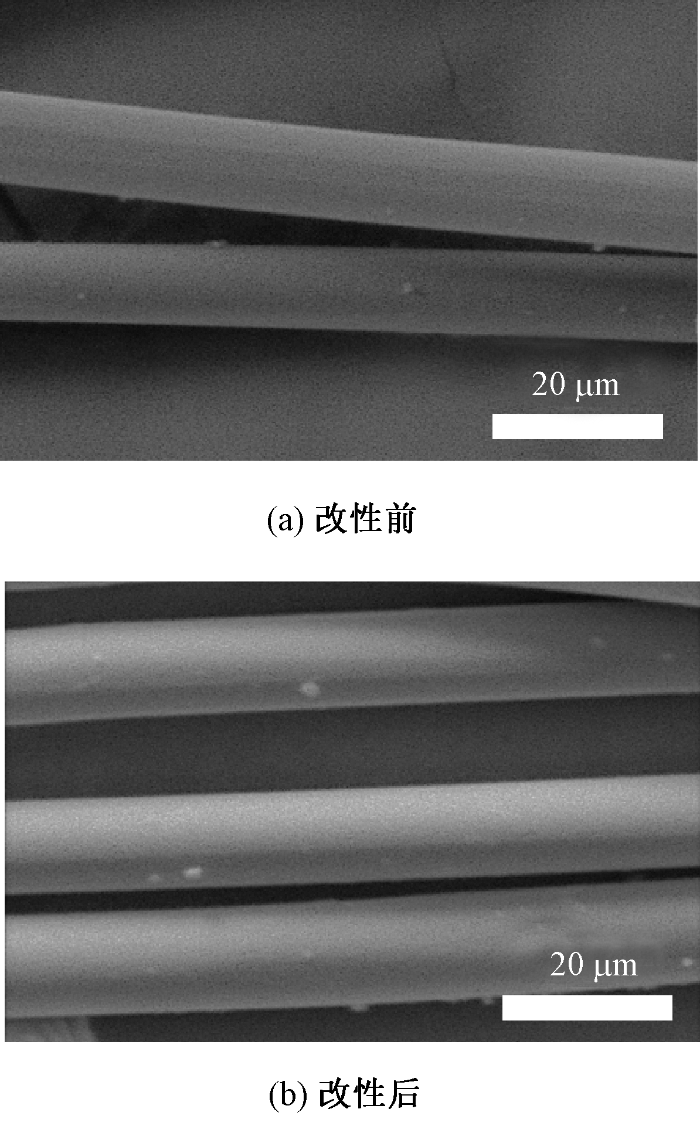
2.2 纤维官能团组成分析
图2
图2
莱赛尔纤维和羧甲基化纤维的红外谱图
Fig.2
FT-IR curves of Lyocell fiber and carboxymethylated fiber
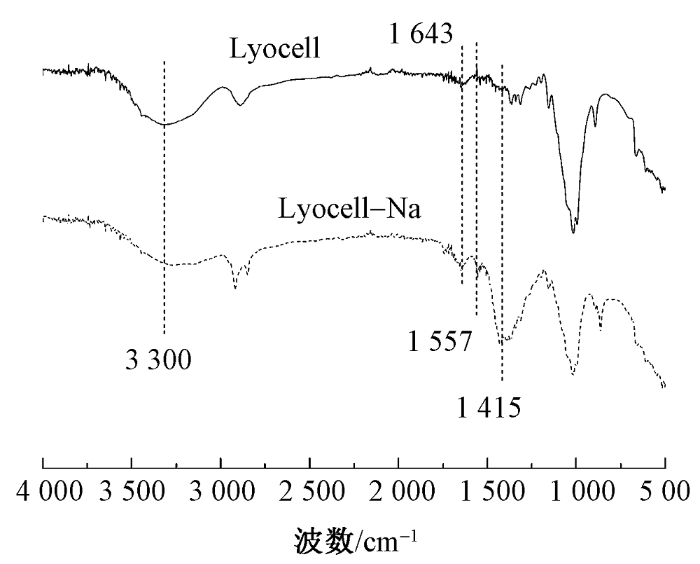
2.3 纤维热稳定性分析
利用热重分析仪对莱赛尔纤维改性前后的热稳定性进行了测试,结果如图3所示。可见2种纤维均存在2个热质量损失平台。第1个热质量损失平台发生在100 ℃左右,这是由于测试样品中均含有一定质量的结晶水;随着温度升高,结晶水逐渐损失。原始莱赛尔纤维第2个质量损失阶段发生在230~380 ℃范围内,其中最大质量损失速率对应的温度为348 ℃;而改性后纤维的第2个热质量损失行为有所提前,发生在197~340 ℃温度区间内,最大质量损失速率对应的温度提前到297 ℃。这可能是因为莱赛尔纤维经过改性后,纤维分子链上大量羟基变成了羧基,且配位有大量钠离子(Na+)。Na+对纤维具有较强的催化降解作用,能促进纤维基体提前降解成炭,同时导致残炭量的增多[23-24]。在700 ℃时,原始莱赛尔纤维的残炭量仅为17.0%,而羧甲基化纤维的残炭量达到了24.4%,相较于原始莱赛尔纤维残炭量提升了43.5%。
图3
图3
莱赛尔纤维和羧甲基化纤维在氮气氛围下的TG和DTG曲线
Fig.3
TG (a) and DTG (b) curves of Lyocell fiber and carboxymethylated fiber in nitrogen atmosphere
2.4 纤维极限氧指数分析
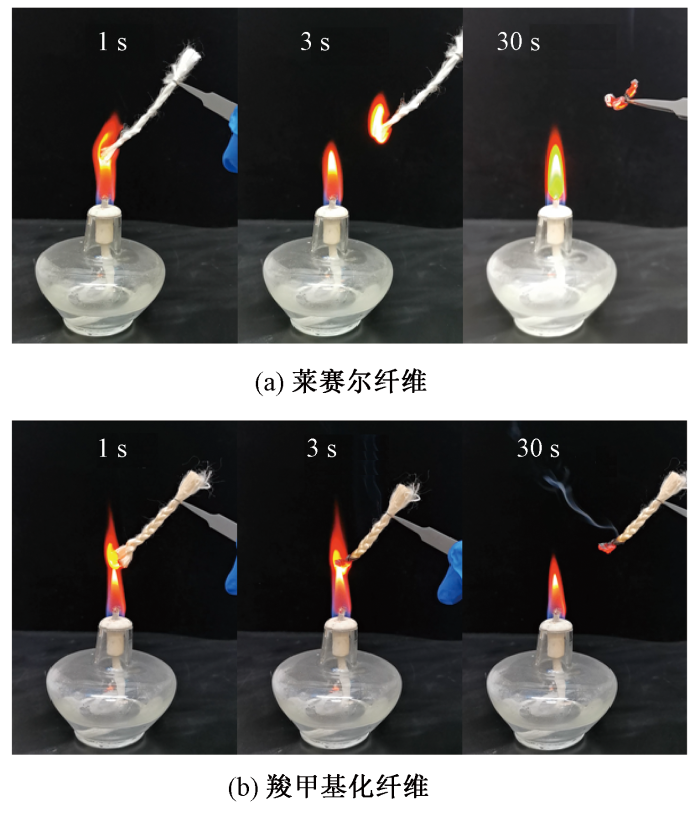
莱赛尔纤维由100%纤维素组成,仅含有C、H、O 3种元素,决定了其具有易燃属性,因此极限氧指数测试仅为(17.8±0.9)%;经过羧甲基化改性后,纤维素分子链上部分羟基变为羧基,且配位有大量Na+,极限氧指数提升至(35.3±0.9)%,金属离子阻燃效果显著。图4示出酒精灯燃烧测试照片。可看出,莱赛尔纤维束在3 s内即被引燃,随后快速燃烧殆尽;而含有金属离子的羧甲基纤维素纤维在持续点燃30 s后未发生燃烧,无连续火焰产生,仅存在微弱的阴燃现象,这可能与纤维密集程度有关:当纤维密集程度低时,纤维间热量传递较弱,火焰传播能力差;而当纤维密集程度高时,由于纤维排列紧密,热量传递连续性增强,因此产生一定的阴燃现象。
图4
图4
酒精灯燃烧测试照片
Fig.4
Photos of alcohol lamp combustion test.
(a) Lyocell; (B) Carboxymethylated fiber
2.5 纤维燃烧性能分析
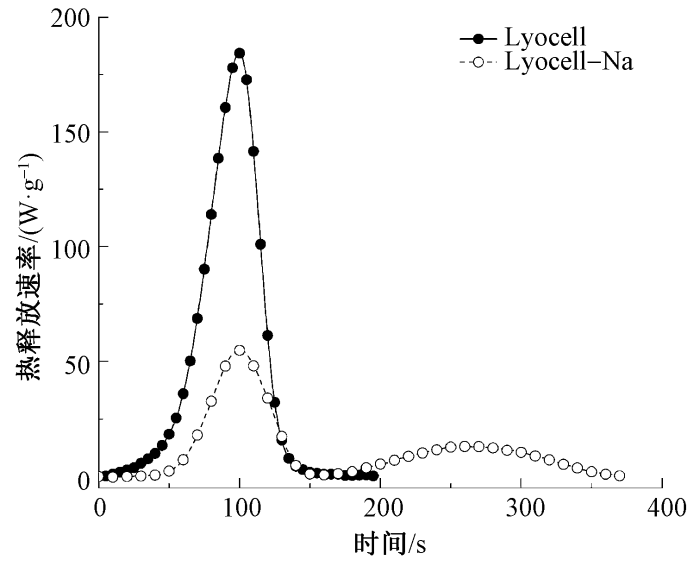
图5示出纤维样品的热释放速率(HRR)曲线。纯莱赛尔纤维热释放速率曲线峰值高且尖锐,说明在燃烧过程中其燃烧剧烈,在短时间内即可释放大量热量。经过羧甲基化改性的纤维热释放速率显著下降,热释放速率峰值从184.4 W/g下降到55.2 W/g,下降幅度为70.1%,且Lyocell-Na纤维呈现出双峰现象,表明其存在一定的凝聚相阻燃机制;第2个热释放速率峰相对平缓,表明Na+在燃烧初期可促进纤维基体炭化,于纤维表面形成致密屏障炭层;当炭层内部热量积累到一定量时会突破炭层,因而形成第2热释放峰。此外,总热释放量和热释放容量分别从8.3 kJ/g下降到4.2 kJ/g,从185.9 J/(g·K)降低到110.3 J/(g·K),降幅分别为49.4%和40.7%,阻燃效果明显。观察燃烧后残炭的形貌(见图6)可发现:Lyocell纤维的残炭松散无形,存在断裂状残炭,整体形貌不够连续;而Lyocell-Na燃烧后的炭层虽然存在一些孔洞,但整体形貌表现出相对致密的结构,具有一定的炭层保护作用,充分证明了羧甲基化改性对纤维素纤维抑制热量产生与释放、降低火灾危险性方面具有实际意义。
图5
图6
图6
莱赛尔纤维及羧甲基化纤维残炭的SEM照片
Fig.6
SEM images of Lyocell (a) and carboxymethylated fiber (b) carbon residue
2.6 纤维力学性能分析
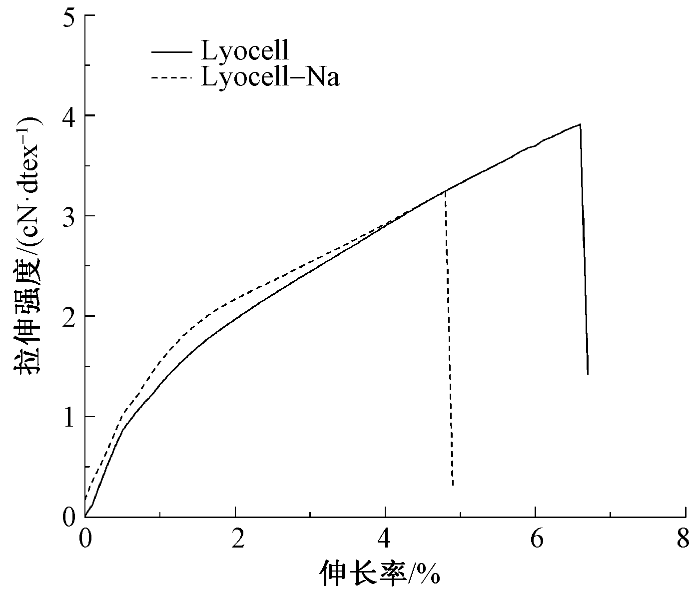
利用单纤维拉伸测试仪对改性前后的莱赛尔纤维进行拉伸性能测试,结果如图7所示。与未改性的莱赛尔纤维相比,经羧甲基化改性后纤维的断裂强度稍有下降,从3.9 cN/dtex下降到3.2 cN/dtex,这可能是由于NaOH进入纤维内部造成部分分子链断裂,引起结晶度轻微下降,从而影响到力学性能。尽管纤维断裂强度有所下降,其整体强度仍可保持在80%以上,力学性能保持良好。
图7
图7
莱赛尔纤维和羧甲基化纤维的拉伸性能曲线
Fig.7
Tensile properties of Lyocell fiber and carboxymethylated fiber
2.7 纤维传感性能分析
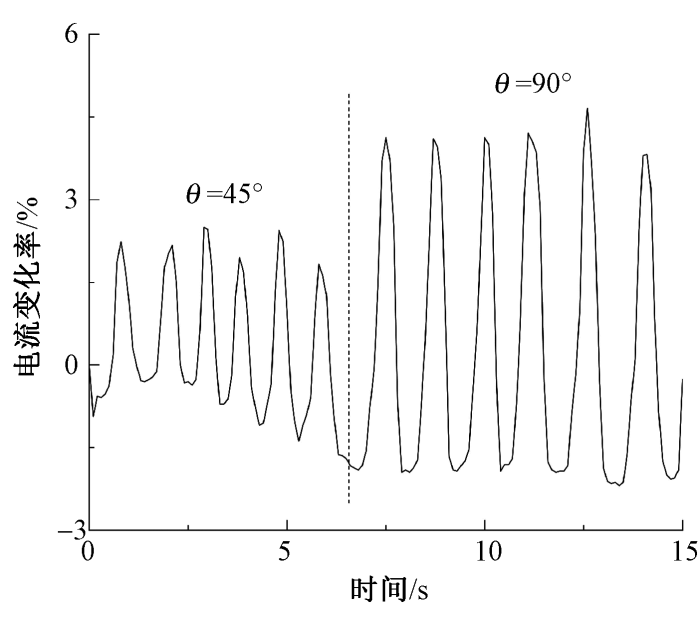
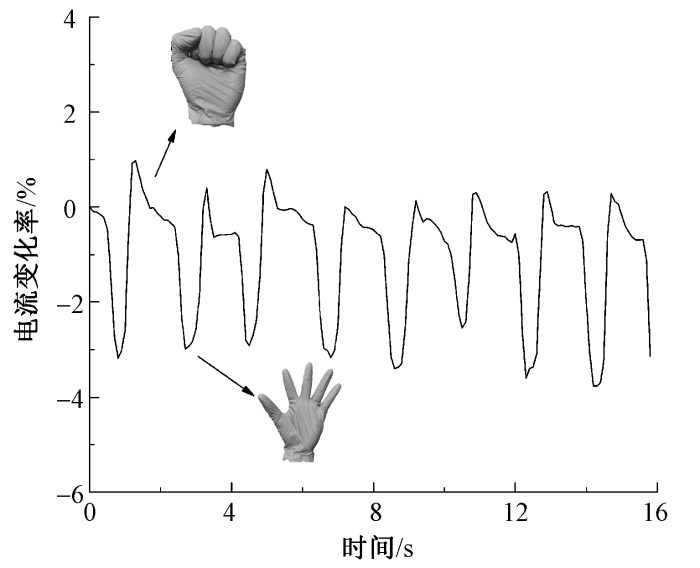
水凝胶纤维的传感性能可通过电流信号的相对变化进行表征,在外界电压作用下,水凝胶纤维内部离子会产生定向移动。当纤维感受到贴合物体发生物理形变时,纤维内离子传输通道随之变化,从而导致电流产生变化。图8示出莱赛尔水凝胶纤维对手指弯曲角度变化的循环响应能力。
图8
图8
莱赛尔水凝胶纤维对手指弯曲角度的响应性
Fig.8
Response ability of Lyocell hydrogel fiber to finger bending angle
当水凝胶纤维被贴合于手指关节处进行弯曲循环动作时,纤维随之产生一定的形变,得到不同电流信号波动,并且对不同弯曲角度具有不同的电流变化率。在样品两端施加电压为3 V时,电流可实现48~51 μA的实际变化值。当手指弯曲角度θ为45°时,电流变化率约为2%;随着弯曲角度增大为90°时,电流变化率随即增大到4%。
图9示出莱赛尔水凝胶纤维对不同手势的识别能力。将水凝胶纤维贴合于手腕处进行手掌握拳和张开手势测试,手腕处会产生微形变,从而引起电流变化,实现手势识别功能。
图9
图9
莱赛尔水凝胶纤维对不同手势的识别能力
Fig.9
Ability of lyocell hydrogel fiber to recognition different gestures
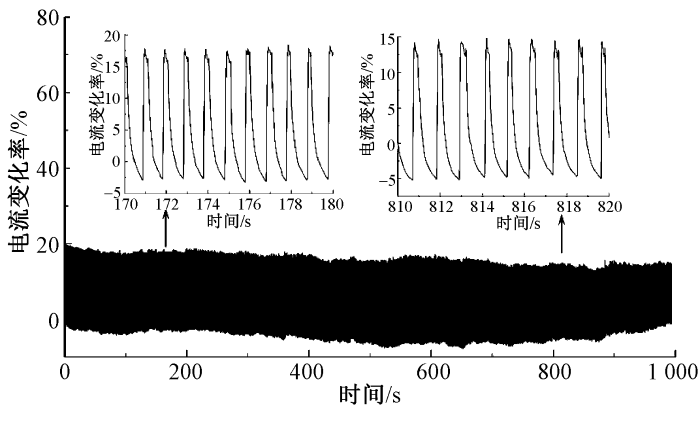
图10示出水凝胶纤维在1 Hz频率下进行循环稳定性测试的结果。
图10
经过1 000 s的循环,水凝胶纤维电流变化率未出现明显衰减,说明该纤维具有较高的稳定性能。综上,莱赛尔水凝胶纤维能精确感应人体动作变化产生的物理形变,对不同形变具有对应的响应信号。
3 结论
本文制备了一种纤维素基水凝胶纤维,由莱赛尔纤维经过醚化反应制得,通过在分子链中引入羧基和金属离子,极大提高了莱赛尔纤维的阻燃性和吸水性,吸水后的纤维对物理形变具有实时传感性能,得到以下结论。
1)莱赛尔纤维经醚化反应处理后,由于引入大量羧基和Na+,金属离子阻燃效果显著,极限氧指数从(17.8±0.9)%提高到(35.3±0.9)%,热释放速率峰值和总热释放量分别下降了70.1%和49.4%。Na+的存在有促进基体成炭的作用,致密的炭层可抑制热量传递和阻碍氧气进入基体内部,从而提高纤维阻燃性能。
2)在热降解过程中,羧基化纤维的最大热分解速率对应的温度有所提前,成炭能力提高;在碱性反应环境下,单纤维断裂强度可保持在80%以上。
3)吸水后凝胶化的纤维具有离子导电能力,在满足阻燃性能的基础上,对不同程度形变可产生对应的电流信号变化、识别动作状态,在柔性传感领域具有较大的发展前景。
参考文献
Advanced flexible materials from nanocellulose
[J].
Functionalization of nanocellulose applied with biological molecules for biomedical application: a review
[J].
High-performance smart cellulose nanohybrid aerogel fibers as a platform toward multifunctional textiles
[J].
Sustainable, thermoplastic and hydrophobic coating from natural cellulose and cinnamon to fabricate eco-friendly catering packaging
[J].
Transparent, intrinsically stretchable cellulose nanofiber-mediated conductive hydrogel for strain and humidity sensing
[J].
Smart Ti3C2Tx MXene fabric with fast humidity response and joule heating for healthcare and medical therapy applications
[J].
DOI:10.1021/acsnano.0c03391
PMID:32644797
[本文引用: 1]

An increasing utilization of flexible healthcare electronics and biomedicine-related therapeutic materials urges the development of multifunctional wearable/flexible smart fabrics for personal therapy and health management. However, it is currently a challenge to fabricate multifunctional and on-body healthcare electronic devices with reliable mechanical flexibility, excellent breathability, and self-controllable joule heating effects. Here, we fabricate a multifunctional MXene-based smart fabric by depositing 2D TiCT nanosheets onto cellulose fiber nonwoven fabric special MXene-cellulose fiber interactions. Such multifunctional fabrics exhibit sensitive and reversible humidity response upon HO-induced swelling/contraction of channels between the MXene interlayers, enabling wearable respiration monitoring application. Besides, it can also serve as a low-voltage thermotherapy platform due to its fast and stable electro-thermal response. Interestingly, water molecular extraction induces electrical response upon heating,, functioning as a temperature alarm, which allows for real-time temperature monitoring for thermotherapy platform without low-temperature burn risk. Furthermore, metal-like conductivity of MXene renders the fabric an excellent Joule heating effect, which can moderately kill bacteria surrounding the wound in bacteria-infected wound healing therapy. This work introduces a multifunctional smart flexible fabric suitable for next-generation wearable electronic devices for mobile healthcare and personal medical therapy.
Functional nanomaterials through esterification of cellulose: a review of chemistry and application
[J].
One-pot cellulose etherification and self-crosslinking via a mild hydroxyl-yne click reaction in a homogeneous system
[J].
Functionalized cellulose for water purification, antimicrobial applications, and sensors
[J].
A lightweight MXene-coated nonwoven fabric with excellent flame retardancy, EMI shielding, and electrothermal/photothermal conversion for wearable heater
[J].
Copper-coordinated cellulose fibers for electric devices with motion sensitivity and flame retardance
[J].
溶胶-凝胶法改性阻燃粘胶纤维的制备及其性能
[J].
Preparation and properties of sol-gel modified flame retardant viscose fiber
[J].
基于层层组装法构建阻燃天然纤维素纤维织物的研究进展
[J].
Research process on preparation of flame retardant natural cellulosic fiber fabric via layer-by-layer assembly method
[J].
Bioinspired,highly adhesive, nanostructured polymeric coatings for superhydrophobic fire-extinguishing thermal insulation foam
[J].
DOI:10.1021/acsnano.1c02254
PMID:34170679
[本文引用: 1]

Lightweight polymeric foam is highly attractive as thermal insulation materials for energy-saving buildings but is plagued by its inherent flammability. Fire-retardant coatings are suggested as an effective means to solve this problem. However, most of the existing fire-retardant coatings suffer from poor interfacial adhesion to polymeric foam during use. In nature, snails and tree frogs exhibit strong adhesion to a variety of surfaces by interfacial hydrogen-bonding and mechanical interlocking, respectively. Inspired by their adhesion mechanisms, we herein rationally design fire-retardant polymeric coatings with phase-separated micro/nanostructures a facile radical copolymerization of hydroxyethyl acrylate (HEA) and sodium vinylsulfonate (VS). The resultant waterborne poly(VS--HEA) copolymers exhibit strong interfacial adhesion to rigid polyurethane (PU) foam and other substrates, better than most of the current adhesives because of the combination of interfacial hydrogen-bonding and mechanical interlocking. Besides a superhydrophobic feature, the poly(VS--HEA)-coated PU foam can self-extinguish a flame, exhibiting a desired V-0 rating during vertical burning and low heat and smoke release due to its high charring capability, which is superior to its previous counterparts. Moreover, the foam thermal insulation is well-preserved and agrees well with theoretical calculations. This work offers a facile biomimetic strategy for creating advanced adhesive fire-retardant polymeric coatings for many flammable substrates.
Combining inherent and additive phosphorus-containing flame retardants for enhancing flame retardancy and smoke suppression effects on polyisocyanurate-polyurethane foam
[J].
Structure and properties of flame-retardant Lyocell fibers prepared by blending method
[J].
磷硅改性阻燃抑熔滴聚酯纤维的制备及其性能
[J].
Preparation and properties of phosphorus-silicon modified flame retardant and anti-dripping polyester fiber
[J].
无卤阻燃热塑性聚烯烃弹性体的研究进展
[J].
DOI:10.19491/j.issn.1001-9278.2023.06.017
[本文引用: 1]

综述了近年来热塑性聚烯烃弹性体材料无卤阻燃的研究进展,介绍了各类阻燃剂对材料阻燃和力学性能的影响。用于热塑性聚烯烃弹性体的无卤阻燃剂以金属氢氧化物阻燃剂和膨胀型阻燃剂为主,磷酸盐类膨胀型阻燃剂应用最为广泛,新型单组分膨胀型阻燃剂已成为发展趋势。
Research progress in halogen-free flame-retardant thermoplastic polyolefin materials
[J].
DOI:10.19491/j.issn.1001-9278.2023.06.017
[本文引用: 1]

This paper reviewed the research progress in halogen⁃free flame⁃retardant thermoplastic polyolefin materials in recent years, and the effect of various flame retardants on the flame⁃retardant and mechanical properties of polyolefin materials were analyzed. These halogen⁃free flame retardants for thermoplastic polyolefin mainly included metal hydroxide flame retardants and intumescent flame retardants, in which phosphate intumescent flame retardants were the most widely used. Nevertheless, the new type of one⁃component intumescent flame retardants has become a trend in future development.
Transforming commercial regenerated cellulose yarns into multifunctional wearable electronic textiles
[J].
Multifunctional 2D-3D heterogeneous MXene@ZIF-8 coated cotton/lyocell blended fabrics for fire protection, motion detection and UV-resistance
[J].
A cleaner and sustainable preparation of green flame retardant and antibacterial lyocell fabric
[J].
沙柳制备高取代度羧甲基纤维素钠的优化和表征
[J].
Optimization and charaterization of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose with a high degree of substitution from salix psammophila
[J].
Enhanced flame retardant performance of poly(vinyl alcohol) composites based on phosphorus-metal ion synergistic effect
[J].
Modification of ramie fabric with a metal-ion-doped flame-retardant coating
[J].




 京公网安备11010502044800号
京公网安备11010502044800号